(30858 products available)

























































































































































































































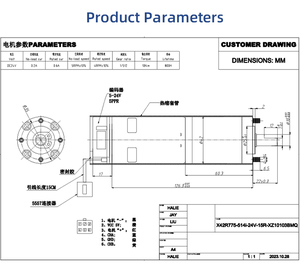






Vector motors are classified differently, depending on the operational method applied to the stator and rotor. The yawning variety is meant to meet other applications' torque and speed requirements. The following are the different types of vector motors and their unique features:
AC Vector Motors
The AC vector motor is designed for applications that need a strong motor with a lot of power. They have come in two principal types, synchronous and asynchronous. AC vector motors control the output by regulating the current phase angle applied to the motor. This allows precise control of torque and speed. Synchronous vector motors offer high efficiency and maintain constant speed, while asynchronous motors are more robust and can work at variable speeds.
DC Vector Motors
The dc vector motor uses direct current to run, with speed variation achieved by altering the voltage applied to the armature and field windings. Dc vector control has better speed and torque control than conventional dc motors. This made it ideal for use in situations that required high-performance motor control, such as robotics and aerospace systems, where precision and reliability are paramount factors.
Brushless Vector Motors
Brushless vector motors are dc motors without brushes. They use an external controller to supply power in a way that produces a rotating magnetic field. This improves the torque and speed control, making them ideal applications requiring high efficiency and long life, like electric cars and aerospace. Consider brushless dc motor with vector control as a precise motor for efficient and controlled operation.
Stepper Vector Motors
Stepper vector motors are used in applications that require accurate position control. They divide the rotation into small steps to achieve precise movement. Their vector control enhances their performance by controlling torque and speed. This makes them suitable for complex machineries, such as multiaxes CNC and 3D printers, requiring precise motion in several directions.
Stator and Rotor Materials
The materials used to make the stator and rotor of a vector motor determine its performance and durability. Most AC vector motors have rotors made from aluminum or silicon steel to maintain high magnetic flux. Those materials are lightweight and highly conductive.
The stators are generally wound from copper wire, which is an excellent conductor of electricity. It has high-density electric field lines, resulting in higher efficiency. Most synchronous vector motors employ silicon steel rotors. The reason is the enhanced magnetic performance properties of this material.
Commutation Components
Housing and Encapsulation
Most vector motors have robust housings made from aluminum alloys or other high-strength materials that aid in heat dissipation. This helps protect the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and debris.
Many vector motors have sealed housings or additional protective covers to increase their life by reducing exposure to potential contaminants. This is important for applications used in extreme conditions.
Cooling Systems
Cooling is vital for vector motor performance and longevity. Many of them have advanced liquid or air cooling systems that help maintain the operating temperature even under excessive load. This prevents overheating and possible damage to the motor's components.
High Performance with Low Cost Operation
Vector motors provide premium performance in precision tasks like CNC machinery and robotics. They can maintain high torque even at low speeds. This leads to smooth, powerful motions without excessive energy use. Vector motors can reduce energy costs, downtime, and wear on connected components.
Versatility for Many Industries
Vector motors drive the same thing in many industries. That makes them valuable for many commercial buyers. Industrial brushless motors control precision mechanics for aerospace or robotics. And they provide variable-speed fans in HVAC systems. No matter the industry, vector motors provide dependable and efficient motion control across various applications.
Savings From Efficient Motion Control
The great precision and control of the vector motor cuts costs associated with excessive motion. It reduces the need for extra gears or mechanical parts. They also reduce energy consumption by limiting excess power. Commercial vector motors also reduce maintenance needs, leading to long component life and savings.
Increased Output and Enhanced System Capability
Vector motors provide greater system output, increasing commercial appeal. Their precision control leads to an increase in the quality of the final product. Vector motors enable the machinery to operate at optimum efficiency. This leads to a decrease in cycle time and waste production in manufacturing contexts.
Reliable Precision Control
Vector motors are chosen for applications demanding reliability in precision control. In aerospace, robotics, and manufacturing, vector motors have to perform mission-critical tasks. They have to maintain speed and torque despite changes in load. Their ability to provide reliable performance in such applications can reduce failure rates and increase operational security.
Low Energy Consumption with High Precision
Vector motors have high precision, which reduces energy consumption. They provide the motor with only as much power as the load demands. This prevents the motor from drawing excessive energy, whether the load is small or big. Thus, it reduces energy costs and lessens the motor's thermal fatigue. High precision control extends the life of vector motors and conserves energy for a sustainable future.
Durability in Harsh Conditions
Vector motors are built for strength, with robust housings that withstand dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures. They continue working where other motors might fail, making them key to reducing frequent replacements and downtime.
Smooth Operation in Sensitive Systems
Vector motors operate smoothly, with no jerks or sudden moves. This gentle power is great for sensitive equipment that needs fine control, such as medical devices and robotics. Even in delicate operations, vector motors provide steady, reliable motion without harming anything they touch.
Endurance Under Heavy Loads
Vector motors are made to work hard without overheating or wearing out, even when carrying heavy loads for hours. Their advanced design lets them handle tough jobs, like lifting big weights in factories or driving complex machines in mining. They help get more work done without breaks, boosting productivity in heavy-duty tasks.
Versatility Across Different Applications
Vector motors are used in many places, from factory robots to space vehicles. Their unique ability to control speed and force precisely makes them useful in many jobs. No matter the industry, vector motors adjust to fit the requirements, ensuring they perform well across a wide range of applications.
Low Maintenance and Easy Care
Vector motors require less care than many other types. With no brushes to replace and strong parts built to last, they often run without needing repairs. This saves time and money for those using them, allowing workers to focus on other important tasks. Thanks to vector motors, there is less worry about how often the motor will need fixing or replacing.
A1: A vector motor is a type of electric motor that provides precise control of torque and speed. It does this by independently controlling the two components of the motor's magnetic field. This allows for more accurate and efficient operation than traditional methods.
A2: Vector motors are used in various applications, including industrial automation, robotics, and electric vehicles. They provide precise control of motion, making them ideal for applications that require high accuracy and speed.
A3: Vector motors can benefit many industries, including aerospace, manufacturing, and healthcare. Their ability to provide precise control makes them useful in many applications, from controlling robotic arms to driving electric cars.
A4: There are two main types of vector motors: AC vector motors and DC vector motors. AC vector motors are used in applications powered by alternating current, while DC vector motors are used in applications powered by direct current.
A5: One of the main advantages of vector motors is their precision control. This allows for more efficient operation and greater accuracy than traditional motors. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high performance.