(4698 products available)



































































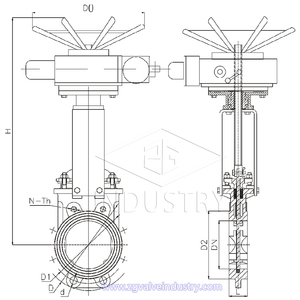
















































































































Valve DN500 is a gate valve that works by lifting the gate out of the way of the fluid path. The gate is the part that controls the flow of the valve. The gate can be made of a variety of materials, including metal, plastic, or a combination of both. The gate valve is designed for full flow when open. When the gate is closed, it shuts off the flow of the valve. This type of valve provides low friction loss and can be used for on/off services or where full flow is needed.
Gate valves work by moving the disc perpendicular to the flow of the pipe. This allows the gate to move up and down, either allowing flow or stopping it.
In the open position, the gate is fully open, allowing the maximum flow of the pipe. In the closed position, the gate is fully closed, stopping the flow. Gate valves can be operated with a handwheel, gearbox, electric motor, or pneumatic actuator. This allows the valve to be opened and closed remotely. Gate valves are commonly found on water, wastewater, and gas applications. They can be used steam and vacuum services as well.
Gate valves can be used in applications where the temperature is between -20 degrees Celsius and 425 degrees Celsius. The pressure of the application also affects the material used in the valve. A gate valve is made of a body, bonnet, and trim. The body is the main part of the valve that connects to the pipeline. The bonnet is the part of the valve that covers the stem and prevents leakage. The trim is the internal parts of the valve that come into contact with the flow of the fluid.
There are several types of gate valves, including the parallel, wedge, or split-wedge. The parallel gate valve has a parallel disc to the flow of the pipe. The wedge is a type of disc that is shaped like a wedge. The split-wedge is a variation of the wedge that allows the gate to flex slightly to achieve a tight seal.
Specification
Maintenance
A well-maintained DN500 valve can improve overall performance and service life. Here are some maintenance tips for DN500 valves:
The wide variety of applications in industries forvalve DN500s demonstrates the importance of choosing the right valve for each job. Here are just a few of the many scenarios where these large valves are used in the industrial world.
The treatment plants that supply clean drinking water to communities often use gate valves because they can completely shut off the water. Butterfly valves are also used when large amounts of water need to flow quickly. Both valve types work well in water distribution pipelines and pump stations. In contrast, check valves ensure that water flows in one direction, which is important in many parts of the water treatment process.
Oil, natural gas, and coal-fired power plants use a variety of valves in their systems. Gate valves are often used to control the flow of fuel into the boilers, while globe, ball, and butterfly valves control the direction and amount of steam flowing from the boilers to the turbine generators. Check valves are very important, especially in the water-cooled heat exchangers.
The chemical industry uses a wide variety of valves to control the flow of many different types of liquids and gases. Gate, globe, ball, and butterfly valves are all used in different parts of the production process. It is very important to choose the right material for the valve and its internal components so that it can handle the often corrosive nature of these fluids.
Hygienic valves are specially designed so that there are no hidden areas where bacteria can grow and contaminate the product. They are often made of stainless steel and have smooth inner surfaces that are easy to clean. Diaphragm and ball valves are often used in the food and beverage industry to meet these stringent hygienic requirements.
Selecting the right DN500 valve requires careful consideration of several critical factors.
Understanding the specific application demands, such as pressure, flow rate, temperature, and media type, is crucial. Different types of valves are designed to perform well under different working conditions.
Choose the appropriate valve type based on the application requirements. For example, ball valves are suitable for on/off control, while butterfly valves are ideal for flow throttling.
Select the proper valve size to ensure adequate flow capacity. Consider not only the pipe size but also the flow characteristics of the system.
Select the proper valve material based on the application's temperature, pressure, and media corrosiveness. Consider materials that can withstand the working environment and ensure long-term reliability.
Choose the appropriate valve operation and control method based on the application requirements. Whether it is manual, pneumatic, electric, or other control modes, it should be able to meet the precise control and automation needs of the system.
Ensure that the valve has excellent sealing performance to prevent leakage and meet the system's safety and environmental protection requirements. Select the sealing material and structure that is suitable for the working conditions and can provide reliable sealing performance.
Select valves that meet relevant industry standards and certifications to ensure product quality and safety. Consider factors such as compliance with regulations, performance testing, and certification to meet the system's requirements.
Q1: What is the difference between a DN and an NPS valve?
A1: The DN and NPS valve sizes are not equivalent. The NPS size is based on the old pipe size, and the DN size is based on the metric system.
Q2: What is a 3-way valve?
A2: A 3-way valve is a valve that can control the flow between three ports. It is often used in complex pipeline systems to switch between different flow directions or to mix or divide fluid streams.
Q3: What is the function of a valve stem?
A3: The valve stem is a rod that connects the actuator to the valve disc. It is responsible for transmitting motion and force from the actuator to the valve disc, allowing the valve to open, close, or adjust the flow.