(16162 products available)


























































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship




















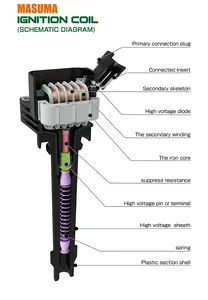


























































Ignition is the system that provides the spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber of an engine. It is a crucial part of an automobile and is primarily found in gasoline-powered vehicles. There are two types of ignition:
Ignition System
The ignition system is further divided into three subcategories:
Conventional Ignition System
In this type of ignition, a 12-volt battery is used to generate current. The system uses a coil that transforms low voltage into high voltage, which powers the spark plugs. Spark plugs are crucial as they create a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. The current is conveyed to the spark plugs through a circuit created by a set of contact points, a condenser, and an ignition switch. This system was widely used in older vehicle models.
Distributor-less Ignition System
In this type of ignition, there is no need for a distributor. It uses two coils that generate current for the engine's four cylinders. This system enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions, making it suitable for modern vehicles.
Coil-on-Plug Ignition System
This is a relatively new type of ignition system that directly powers the spark plug situated on top of the ignition coil. It eliminates the need for distributors and plug wires, allowing for better engine performance. The coil-on-plug ignition system is popular in high-performance vehicles.
All three types of ignition systems play a crucial role in controlling emissions and engine performance. They achieve this by powering the spark plugs and creating a spark at the right time to light the air-fuel mixture.
Types of Diesel Engines
Diesel engines use high-pressure ignition to ignite the fuel. In this type of diesel engine, the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber containing compressed air at high temperatures. The high pressure from the piston and the high temperature from the compression cause the fuel particles to ignite spontaneously.
Due to its simplicity, the high-pressure ignition system is widely used in heavy-duty vehicles, industrial applications, and marine engines. It offers high thermal efficiency and is suitable for applications that require high torque and reliability.
Ignition systems have different specifications depending on the type of vehicle and its engine requirements. Below are some general specifications of various types of ignition systems:
Voltage
Regardless of the type of ignition system, the voltage produced is high. It is approximately between 12 and 45 volts. The high voltage makes it possible for the current to jump the distance between the electrodes in the spark plug.
Current
The current produced in all types of ignition systems is low. The current ranges between 0.5 and 10 milliamps. A current of 0.5 to 10 milliamps is enough to produce a spark that ignites the fuel in the engine.
Duration of the Spark
The spark duration varies depending on the type of ignition system. Systems like the capacitive discharge ignition produce a spark that lasts between 5 and 10 milliseconds. The longer spark duration helps to ignite fuel efficiently. As a result, the vehicle operates efficiently.
Spark Energy
All types of ignition systems produce spark energy ranging between 1 to 10 millijoules. This energy is enough to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine.
Spark Voltage and Current
The voltage and current of the spark produced by ignition systems vary according to the design and components of the system. High-voltage and high-current sparks are produced by ignition systems with a coil, for example, the battery ignition system. On the other hand, lower voltage and current sparks are produced by ignition systems with no coils, for example, the magneto ignition system.
Below are some general maintenance tips for different types of ignition systems:
When choosing the right ignition system for a vehicle, consider the following:
Vehicle
The vehicle's make, model, and year of production should be considered. Some vehicles come with ignition systems designed for compatible systems.
Engine Type
For example, gasoline engines are the most common and require traditional or coil-on-plug ignition systems. In contrast, diesel engines may require glow plugs in addition to an ignition system.
Performance Requirements
Consider the performance needs. High-performance vehicles may benefit from upgraded ignition systems. Such systems provide more power and deliver a stronger spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
Fuel Type
Vehicles running on alternative fuels such as propane or ethanol may require modified ignition systems. This is to accommodate the different properties of the fuels.
Environmental Regulations
Deal with local regulations. Some areas have stringent emissions standards. Therefore, the ignition system chosen should comply with the emissions regulations.
Climate Conditions
Consider the climate where the vehicle will be used. In extreme weather conditions, cold or hot, ignition systems that are resistant to such conditions are needed.
Reliability and Durability
For critical components, ignition systems are essential. Therefore, reliability and durability are equally important in choosing the right ignition system.
Starting and Stopping
Consider how often the vehicle needs to start and stop frequently. In this case, ignition systems that are suitable for such operating conditions should be chosen.
Cost
The cost of the ignition system and its components, as well as maintenance and repair costs, should be considered.
Upgrades
If there are future plans to upgrade the vehicle for better performance, the ignition system chosen should be compatible with the planned upgrades.
The following are the types of ignition DIY replacement instructions:
Ignition coil
Coil-on-plug: To replace an ignition coil that is on top of the spark plugs, loosen the bolts, and carefully pull it straight up without damaging the plugs. Then, gently push the new coil down until it is flush with the plugs and tighten the bolts. Coil pack: First, disconnect the battery. Then, remove the cables and bolts holding the coil pack. Take out any screws holding the ignition control module and swap in the new one.
Ignition switch
First, disconnect the battery. Find the ignition switch under the steering column and remove the trim. Loosen the screws holding the switch and slide it out. Unplug the connectors and plug them into the new switch. Then, slide the new switch into place and tighten the screws.
Distributor cap and rotor
First, take a photo to remember where the spark plug wires go. Then, pull the wires off the cap and remove the cap by loosening the bolts. Take out the old rotor and replace it with a new one. Put the new cap on and tighten the bolts. Then, put the wires back on in the same order as they were on the old cap.
Starter motor
First, disconnect the battery. Then, remove the motor's cables and the bolts holding it in place. Take the starter motor out and put the new one in. Then, tighten the bolts and reconnect the cables.
Q1. What are the most common problems with ignition systems?
A1. The most common problems are usually related to wear and tear. For instance, faulty spark plugs, which may show up as an engine misfire or difficulty starting the engine. Other issues could be weak ignition coils, which provide insufficient power to the spark plugs, or dirty air filters that restrict airflow, affecting the engine's performance.
Q2. How can one troubleshoot ignition system problems?
A2. To troubleshoot, start by checking for any dashboard warning lights. A diagnostic tool can read error codes from the vehicle's computer. Physically inspect components like spark plugs and coils for visible damage. Listen to the engine while it's running—misfires may be audible. Check the battery voltage. A weak battery can cause starting issues.
Q3. Do different engines require different ignition systems?
A3. Yes, the types of ignition systems used can vary based on engine design—particularly the fuel type and the number of cylinders. For example, diesel engines rely on compression for ignition and don't use spark plugs, while gasoline engines almost always use spark plugs. High-performance engines often need more advanced ignition systems to provide consistent power and efficiency.
Q4. How often should ignition components be replaced?
A4. It largely depends on the component's type and material. For example, copper spark plugs might last 20,000 miles, while iridium plugs can go 60,000 miles or more. Other components like ignition coils are usually replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles as a preventive measure. Always refer to the vehicle's manual for recommended maintenance schedules.
Q5. Can changes to the ignition system improve fuel efficiency?
A5. A well-tuned ignition system ensures complete fuel combustion, optimizing power and efficiency. While minor tweaks can be made for performance vehicles, major changes aren't advisable. Upgrades, like high-performance ignition coils, can improve a vehicle's performance. However, it's essential to ensure any modifications are compatible with the vehicle.