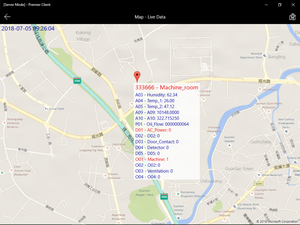
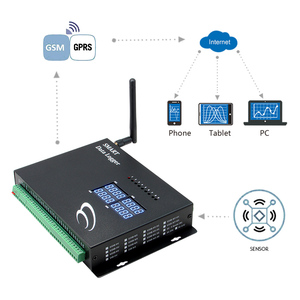
Types of telemetry gsm gps gprs
Telemetry GSM GPS GPRS is a technology that combines several components to monitor and track remote assets. Telemetry involves the automatic measurement and transmission of data from one location to another. GSM, which stands for Global System for Mobile Communications, is a standard for mobile communication. GPS, the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system that provides accurate location information. GPRS, General Packet Radio Service, is a mobile data service on 2G and 3G GSM networks that enables reliable internet connectivity.
This technology allows for real-time monitoring and tracking of various parameters, such as location, speed, and environmental conditions. It has become increasingly popular in various industries, including logistics, transportation, agriculture, and healthcare, where remote monitoring and tracking are crucial for efficiency and safety.
- Telemetry: Telemetry is the technology that automatically collects and transmits data from remote objects. This technology allows for monitoring and analysis of remote objects.
- GSM: GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications. It is a standard developed for mobile communications in the 1980s. GSM is used in mobile communications.
- GPS: GPS is the Global Positioning System. It is a satellite-based navigation system that provides accurate location information. GPS is used for accurate location tracking and navigation.
- GPRS: GPRS stands for General Packet Radio Service. It is a mobile data service on 2G and 3G GSM networks that enables reliable internet connectivity. GPRS allows for low-speed data transfer over mobile networks.
Specification & Maintenance of Telemetry GSM GPS GPRS
Telemetry GPS trackers use a variety of specifications to offer reliable, accurate location data. Here's a detailed look at the specifications:
-
1. Frequency Bands
GPS telemetry devices are designed with the GSM network's frequency bands, allowing communication over mobile networks. The frequency bands include 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz.
-
2. Power Supply
Telemetry devices use a power supply of 3.7V lithium batteries. The batteries are rechargeable, making them convenient for long-term use. Additionally, the power supply can support continuous operation and low power consumption.
-
3. Current Consumption
Current consumption measures how much current a telemetry device uses during operation. Lower current consumption is important for battery-powered devices. Consequently, these devices can support long-term use without frequent battery charging or replacement. Telemetry devices have different current consumptions, including working current (10-50mA), standby current (10-20uA), and sleep current (1uA).
-
4. Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is vital for outdoor telemetry devices exposed to harsh weather conditions. The telemetry devices have an operating temperature of -40°C to 85°C. This range ensures optimal performance even in extreme weather conditions.
-
5. Dimensions and Weight
Telemetry GPS devices are designed to be compact and lightweight for easy integration into various applications. They measure 70mm x 50mm x 20mm in size and weigh 100 grams. The small size and lightweight enhance portability.
-
6. Data Transmission Rate
The telemetry devices have a data transmission rate of 100-200kbps, enabling reliable and fast data communication. The telemetry devices use a GPRS class 10/11 with a maximum data rate of 40-120 kbps.
-
7. Antennas
Different antennas are used in telemetry devices to enhance communication and data transmission. The antennas include a GSM antenna (2dBi gain), GPS antenna (28dBi gain), and a Wi-Fi antenna (5dBi gain). The antennas are essential components of telemetry devices, enabling reliable and fast data communication.
Here are some of the key maintenance requirements for telemetry devices:
- 1. Regular inspections: Telemetry devices should be inspected regularly to identify any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. During the inspection, all components, including antennas, sensors, cables, and housings, should be checked.
- 2. Cleaning: The telemetry devices should be cleaned regularly to remove dust, debris, and dirt. The cleaning enhances optimal performance and prevents damage. Non-abrasive materials and mild cleaning solutions should be used during the cleaning.
- 3. Firmware and software updates: The firmware and software of the telemetry devices should be updated regularly. The updates enhance bug fixes, improvements, and new features.
- 4. Battery maintenance: The telemetry devices' batteries should be maintained regularly. The maintenance ensures optimal performance and extends battery life. The batteries should be checked regularly to identify signs of wear or damage. Additionally, the batteries should be replaced when worn out.
- 5. Environmental monitoring: The telemetry devices should be monitored regularly to ensure they operate within the specified environmental conditions. The environmental conditions include temperature, humidity, and vibration.
- 6. Cable management: The telemetry devices' cables should be managed to prevent tangling, damage, or wear. The cables should be routed and secured properly to prevent interference with other components.
- 7. Documentation: The telemetry devices should be documented to track maintenance activities, inspections, and repairs. The documentation makes it easy to monitor the devices' performance and identify trends.
How to Choose Telemetry GSM GPS GPRS
Selecting the correct telemetry GSM GPS GPRS device for a specific application can be complex, considering the various options available and the technical aspects involved. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing telemetry GSM GPS GPRS:
- Application requirements: Initially, the essential requirements of the application need to be determined. The critical factors include the tracking frequency, the data's size and type, its real-time urgency, and the monitored asset's nature and location.
- Network coverage and reliability: The telemetry device should provide adequate network coverage for the asset's monitoring area. It should also consider the network's reliability and stability, especially in critical applications where data transmission consistency is essential.
- Power consumption: Power consumption is a vital factor in selecting telemetry devices, especially for remote or mobile assets using battery-powered devices. Devices with lower power consumption, such as those with energy-efficient designs or power-saving modes, should be considered.
- Size and installation: The telemetry device's size and ease of installation are critical in applications with space constraints or where the device needs to be quickly installed in various locations. Compact and versatile devices with various installation options and accessories can facilitate the device's fast and straightforward installation.
- Data security and reliability: In many applications, data security and reliability are critical. When selecting a telemetry device, encryption, authentication, and other security features should be considered to ensure data confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
- Cost-effectiveness: Finally, the cost-effectiveness of the selected telemetry device should be considered. Besides the initial purchase cost, the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and data service fees, should be evaluated to determine the most suitable and economically viable solution.
How to DIY and Replace Telemetry GSM GPS GPRS
Telemetry GSM GPS GPRS can be replaced easily, provided that the correct procedures are followed, and the right tools are available. Before starting the replacement, ensure that the new device is fully charged. The tools needed for the replacement process are a screwdriver, prying tools, and sim card ejector. Below are the steps on how to replace Telemetry GSM GPS GPRS:
- Turn off the vehicle's ignition before the replacement begins.
- Remove the screws that hold the device using a screwdriver.
- Use a prying tool to loosen the device and remove it from its place.
- Use a sim card ejector to push the pin into the hole and eject the sim card.
- Put the new device into its place and power it on.
Q and A
Q1: How accurate is GPS telemetry?
A1: GPS telemetry has a high level of accuracy, but several factors can affect its precision. For instance, satellite signal obstructions, atmospheric conditions, and tree cover can influence the accuracy of GPS telemetry data.
Q2: Can users track their pets using GPS telemetry?
A2: Yes, GPS telemetry can track pets if they are fitted with GPS telemetry collars. These collars allow pet owners to monitor their pet's location and movement through GPS data.
Q3: What is the difference between GPS telemetry and regular GPS tracking?
A3: Telemetry GPS is a tracking system that continuously transmits data over long distances, while regular GPS tracking only provides the user's location data at a specific time.