(128 products available)


































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship























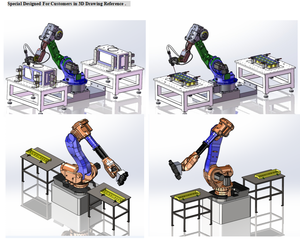
Robos are robotic arms in laser machines that help them to perform tasks with more precision and accuracy than their human counterparts. These machines are already ample and powerful machines, and when paired with a laser, the possibilities of what it can accomplish with more control and precision are boundless.
The robo laser comes in various forms to meet the needs of different kinds of industries. The following are some common types of an application of a laser that could be paired with a laser machine:
Fiber Laser:
All fiber lasers are based on optical fibers, their cores, and their claddings. This makes them efficient and ideal for use in the metal industry, including welding, cutting, marking, etc.
CO2 Laser:
CO2 lasers use carbon dioxide as the primary gas in the laser beam generation. Foe visible light reflection and amplification, other gases such as helium, oxygen, and nitrogen might also be used to enhance performance. This particular laser is highly popular because it's used to cut, weld, and engrave non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, glass, etc.
COE Laser:
This is a semiconductor-pumped solid-state laser that's mass-produced in the industry with the help of low-cost nanosecond pulse generation technology. It's applied to metal surfaces with the primary aim being to mark them. It's also used to weld and cut objects.
UV Laser:
A UV laser has a shorter wavelength than a fiber or CO2 laser. This higher energy of the radiation bursts makes it easier to make precise cuts with minimal damage to surrounding material. In other words, when used to cut something, it needs no real contact, unlike other kinds of lasers. This makes it an excellent choice for delicate materials, including polycarbonate, which is known to warp under the heat of regular lasers.
Fiber lasers are the most common type in the industrial laser market and are used to cut metals like steel, aluminum, copper, etc.The features of a laser cutting machine determine its capabilities and performance.
Robo laser maintenance is critical to minimizing downtime and ensuring that the machine can continue to produce high-quality cuts. Routine maintenance for a laser cutting machine includes the following:
Robotics are widely used in the manufacturing industry. An area where they are extensively used is in cutting applications. With laser cutting, a laser-cutting robot is used to cut products with lasers precisely. This can be used to cut metals like steel, aluminum, titanium, etc. as well as non-metals like plastics, rubber, glass, wood, etc. These can be set on an assembly line where they cut components that can then be put together to make a finished product.
The most common use of a laser-cutting robot is in welding applications. These lasers can be programmed to cut materials at precise angles for easy assembly or to cut intricate patterns and designs into materials that would otherwise be difficult to get through without compromising quality.
A great advantage of a robot laser cutter is that it can be easily integrated with other systems. For example, a material handling system can be connected to a laser-cutting system so that once the material is cut, it is then relocated automatically to wherever it needs to be in the assembly line. Quality assurance systems using AI may also be connected to a laser-cutting system to ensure that the cuts are being made accurately. If any errors are detected, the system can be programmed to notify the personnel so that they can take the appropriate action.
Robos laser cutters are also used in industries other than manufacturing. They are widely used in the automotive industry, jewelry-making, furniture-making, advertisement and signage, medical-related businesses, and electronic industries, to name a few. In the automotive industry, for example, the structural components of the vehicle are laser cut using a robot to achieve maximum precision and quality. Again, the jewelry industry makes extensive use of these machines to cut designs intricately and create those beautiful patterns on jewelry pieces.
Choosing a suitable laser robot requires careful consideration of various factors. These factors ensure that the selected machine will meet specific operational needs while delivering optimal performance levels.
Application Requirements:
The first step in selecting a laser robotic machine is to identify the application requirement. This involves considering what tasks the robot will perform. For instance, a laser-cutting robot for metal will have different specifications than one designed for cutting soft materials like foam or fabric. It's also important to consider the material's thickness that the robot will work with. Higher thickness may require a more powerful laser. Another aspect of the application requirement is the desired level of precision and intricacy of cuts. Some applications may require high-tolerance cuts with complex designs, which means the need for a laser robot with more advanced capabilities.
Laser Type and Power:
Once the application requirements are established, the next step is to decide on the type of laser and its power. Several types of lasers are available for robotic use, each with its advantages.
The CO2 laser is known for its versatility and is suitable for cutting various non-metal materials like plastics, wood, and glass. Fiber lasers are preferred for their efficiency and high-speed cutting capabilities, particularly for metal materials such as steel, aluminum, and copper. Green lasers offer a high level of precision and are ideal for intricate cuts in delicate materials.
Laser power plays a crucial role in determining cutting speed and capacity. Higher-power lasers can cut through thicker materials more quickly but also consider factors like energy efficiency and operating costs.
Robot Arm:
The next thing to look is the design and specifications of the robot arm. The robotic arm design will depend on the application it is to be used for, e.g., if the laser is for welding, a different arm design is required as opposed to one created for cutting. The weight capacity of the arm is another important consideration, as it must be able to support the laser's weight along with any additional tooling or sensors.
Integration and Compatibility:
It's important to consider how well the robot laser will integrate with existing production lines and systems. This includes checking that the machine is compatible with current materials handling equipment. For instance, software communication protocols are required to ensure seamless interaction between different components.
Safety Features:
Finally, when choosing a laser robo, the safety features have to be included. This is important because, as mentioned earlier, lasers can be potentially harmful. It's crucial to select the laser robot with adequate safety measures such as enclosed workspaces, sensors, and emergency stop systems.
Q1: What does a laser robot itself do?
A1: Laser robots can cut and weld metals. Their specific function depends on the end attachment they carry and the task they are programmed to carry out.
Q2: Why are laser robots used?
A2: They are highly accurate and can carry out intricate tasks with great speed. This makes them ideal for cutting, welding, and engraving applications. They also reduce human exposure to hazardous environments.
Q3: What is the difference between laser cutting and regular cutting?
A3: Laser cutting offers greater precision with finer details and cleaner cuts. It is also a contactless method that does not exert any force on the material. Regular cutting methods usually involve high physical contact, which can damage the material.
Q4: What is the highest-powered laser cutting machine?
A4: CO2 lasers are preferred in industries that require high-powered laser cutting, such as the metal and manufacturing industries, because they can produce a higher laser power compared to others.