(420 products available)








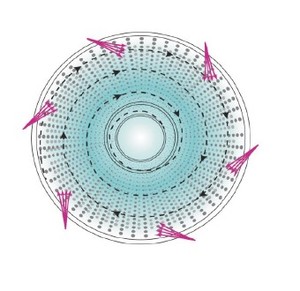









































































































































Types of Jet Mill Grinders
A jet mill uses high-pressure air to grind materials into extremely fine powders. One of the main advantages of jet mills is that they can achieve very high levels of fineness. Products with an average particle size of 10–15 microns and a 95% pass rate can be as high as 50–55 microns. They also have the advantage of low contamination because no internal parts come into contact with the material being ground. Jet mill grinders also have higher specific energy than burrs or hammer mills, which means they can be used to grind very hard materials like ceramic raw materials, lithium iron phosphate, corundum, etc., even to fine powders. They are also typically more efficient than other types of mills for fine milling applications.
Jet mills can be divided into five main types based on their key functional design and how they operate:
Chemical Jet Mill Grinder
Specifications for a chemical jet mill grinder may vary by brand, but in general, a 50- to 100-kg/h capacity machine with an air compressor capable of providing 9 to 10 m3/min at 7 to 15 kgf/cm2 is sufficient for chemical jet milling. The average input particle size is 100 mesh, and the output particle size is 10-45 micro-powders.
Food Jet Mill Grinder
A food jet mill grinder usually has input and output port diameters of about 50 and 40 mm, respectively. The motor power is around 37 kW, and the grinding chamber pressure can be as high as 0.325 MPa. Its capacity is about 300 kg/h. Air volume should be 0.3-0.399 m3/min with the grinding pressure between 0.2-0.3 MPa. Its grinding part typically has a spiral design to improve the flow and ensure a comprehensive grind to produce a particle size between 4 and 60 mesh.
Mineral Jet Mill Grinder
The motor power of a mineral powder jet mill grinder can be found in two categories: high power, over 90 kW, processing capacity mineral powders in a more extensive industrial scale, and lower power of about 22-90 kw for processing smaller batches of mineral powders. The maximum capacity is about 5,000 kg/h. The air volume should be 3-4 m3/min with the grinding pressure around 0.4-0.5 MPa.
The primary care for the jet mill is to inspect, clean, lubricate, and do the repair service parts. Wash the grinder with water and detergent instead of chemicals to avoid inhaling harmful substances. Use air compression, rags, and brushes to clean it thoroughly. Only non-corrosive lubricants should be used to grease the moving parts of the mill. Ensure that any moving parts of the machine are adequately protected from any foreign objects so that they do not cause accidental injury or damage.
A chemical jet mill grinder may crush an extensive range of chemicals from 10 to 50,000 mesh, including calcium carbonate, alumina, quartz, diatomite, barite, clay, zeolite, bentonite, talc, kaolin, silicon carbide, graphite, polymer, nitride, and pesticides. Industrial chemical-grade calcium carbonate is produced using a chemical jet mill grinder. Some machines have special parts to process PCE and PVC plastic solid powders. When servicing the chemical jet mill grinder, it is better to segregate chemicals and avoid the cross-contamination of chemical residues.
Industrial jet mills play a crucial role in various sectors by providing fine powder milling solutions. Here are some industry scenarios where jet mill grinders are commonly used:
There are several factors manufacturers need to consider when choosing the right jet mill grinder for their application.
Material characteristics
The mill's feeding nozzle dimension and mill chamber diameter must correlate with the powder's material features. The jet mill's geometry should also suit the material attributes, including morphology, density, tenacity, and moisture content. For instance, a brittle material with high moisture content will clump together and require a different-shaped mill to perform efficiently.
Desired particle size distribution
Different jet mills operate best within certain particle size ranges. Buyers need to choose a mill that can achieve the desired powder size. Also, they have to consider if your process can handle the additional steps needed to filter or segregate the intermediate particles.
Material of construction
Operators must select the jet mill construction material spec that will incur minimal wear and tear while coming into contact with the milling material. A stainless steel jet mill is the ideal choice for an abrasive material, like ceramics, that cause high wear. Still, a carbon steel may suit a non-abrasive material.
Cleaning requirements
Powder production plants often switch between milling materials. For this reason, many operators prefer a jet mill that can easily undergo cleaning cycles. According to plant production needs, a mill with manual cleaning may suffice. However, a fully automated cleaning system is preferable when jet mill grinders come into contact with toxic or flammable material.
Budget constraints
Generally, jet mills are more expensive than mechanical mills. Within the jet mill category, buyers need to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each type and select the one that offers the most value for their investment.
Q1 What are some benefits of jet mill grinders?
A1 Jet mill grinders have many benefits. The mills crush materials without any contact between the parts. Therefore, the grinders are ideal for fragile or brittle materials. Jet mill grinders have a simple design with few moving parts, making them easy to maintain and clean. The mills produce fine powders of up to 10 microns and have a high milling efficiency. Jet mills use compressed air or gas as the milling medium, making them energy efficient.
Q2 What materials do jet mill grinders process?
A2 Jet mill grinders process various materials to produce fine powders. The mills crush tough and hard materials, such as ceramics and minerals. They also process fragile materials like dry milk, chalk, and limestone. Jet grinders are suitable for pulverizing materials with high hardness levels, such as titanium dioxide, zeolite, silicon carbide, glass, and carbon black. Jet mill grinders are also used to reduce the size of materials in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Q3 What are the limitations of a jet mill?
A3 Despite the advantages of jet mill grinders, there are some limitations. The initial cost of installing the mills can be high. Operators may need training to understand the proper installation and functioning of the grinder. Although the grinding process is dry, the material may require prior dewatering or drying.
Q4 How safe are jet mills?
A4 Jet mills are generally safe. There is no contact between the particles and the grinding media. However, precautionary measures are essential. Operators must take precautions because fine powder particle size is highly explosive.