(149201 products available)






















































































































































































































Igniter parts are essential components in various devices, particularly those that require a combustion process to initiate a fire. These parts are utilized in numerous applications, including automotive engines, gas burners, and even some types of internal combustion engines. Given their critical role in starting combustion, understanding the different types of igniter parts and their functionalities is essential for anyone involved in maintenance, repair, or even the manufacturing process.
It is important to know the specifications of the parts of the igniter that are going to be used in order to meet the needs of specific applications. Here are the specifications of the different parts of the igniter, including the spark plug:
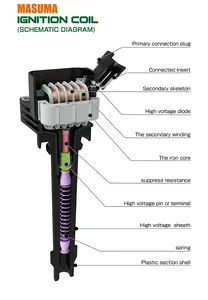
Ignition coil:
The voltage output of an ignition coil varies depending on the type of coil and the design of the ignition system. Most coils generate between 12,000 and 45,000 volts, with some high-performance coils exceeding 100,000 volts. The resistance of the primary and secondary windings is typically between 0.5 and 3 ohms for the primary and 7,500 to 15,000 ohms for the secondary.
Ignition module:
The ignition module controls the timing and duration of the ignition spark based on inputs from various sensors, such as the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor. It also monitors engine operating conditions, such as temperature and load, to optimize ignition timing. The module typically operates within a voltage range of 8 to 16 volts and consumes around 200 to 500 milliwatts of power.
Distribution cap and rotor:
The material used to make the distributor cap and rotor can affect their performance and lifespan. Common materials include thermoplastic, thermoset, and carbon-impregnated materials, each with varying durability and resistance to wear. The rotor's design, including the number of terminals and rotor arm shape, is tailored to match specific ignition systems and engine configurations.
Ignition wires:
Ignition wires have different resistance levels that affect signal strength. The resistance of high-performance wires is typically low, around 50 to 150 ohms per foot, while stock wires range from 500 to 1,500 ohms per foot. The insulation material's heat tolerance varies, with silicone wires able to withstand temperatures of up to 200°C (392°F) and other materials offering lower heat resistance. Ignition wires also come in different lengths to fit various engine layouts, with typical lengths ranging from 24 to 36 inches (61 to 91 cm).
Spark plug:
Spark plugs come in different heat ranges, such as hot, medium, and cold. Hot plugs have a heat range number between 70 and 80, while cold plugs have numbers between 10 and 20. The electrode gap varies depending on the engine type, with gaps ranging from 0.7 to 1.1 mm (0.028 to 0.043 inches). Spark plugs are also made from different materials, such as copper, nickel, platinum, and iridium, each with varying durability and performance characteristics.
Maintaining ignition parts is vital to ensure proper engine performance and efficiency. Here are some general maintenance tips:
Following these maintenance tips can help keep the ignition system components in good condition, ensuring reliable engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Before purchasing igniter components for resale, business buyers need to understand the elements that influence the choice of these parts. Here are some of them:
Power Output
Igniter components have different power outputs. Choose components with higher power outputs if targeting customers with high-performance or specialty vehicles. Standard vehicle engines do not require high-power igniters. As such, igniter parts with lower power outputs are suitable for vehicles with standard engine performance.
Fuel Type
The type of fuel that powers a vehicle also influences the choice of igniter parts. Diesel engines, for instance, require more powerful and robust igniter components because they rely on compression to ignite. Whereas, vehicles powered by gasoline or petrol do not need as much power from the igniter to fuel the engine.
Engine Size and Type
Generally, larger and more powerful engines require more powerful and complex ignition systems. Choose components for larger engines that can handle the increased demand for power and ignition. Additionally, pick components based on the engine type. For example, choose coil-on-plug components for modern vehicles with petrol engines and an engine with a distributor for older vehicles.
Material and Construction
The material and construction of the igniter parts also need to be considered. Components made from durable materials such as high-strength steel and aluminum are long-lasting. They can withstand the harsh conditions of the engine. However, the material influences the cost of the part. More igniter parts made from premium materials are expensive. Therefore, choose igniter parts with a material that balances quality and affordability.
Brand and Quality
Lastly, choose igniter parts from reputable brands with high reviews. Such brands focus on quality to maintain their clientele. Additionally, pick components based on quality. Premium components last longer and reduce the frequency of replacement. They also ensure that the vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Therefore, by targeting high-end customers, they will be looking for premium igniter components.
Replacing a gas stove igniter is a straightforward process that can be done with a few basic tools. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Q1: How do you know if an igniter part is bad?
A1: There are several signs that show a bad igniter part. For instance, if the engine keeps cranking but won't start, it could be a sign of a bad spark plug or a worn-out ignition coil. Other signs include a rough idle, lack of acceleration, a check engine light, and hard starts. Visibly worn-out parts, like cracks on the ignition coil, can also signal bad igniter parts.
Q2: Can users fix igniter parts by themselves?
A2: While some igniter parts are easily accessible and manageable, like changing spark plugs, other parts, such as the ignition timing system, are more complex. Depending on a vehicle's make and model, the ignition timing system could be a more complex mechanical part. Igniter parts that require more disassembly or specialized tools and knowledge to diagnose and repair are not recommended to be handled by users themselves.
Q3: How often should igniter parts be checked?
A3: Igniter parts should be checked during regular maintenance schedules, such as oil changes or every 5,000 to 7,500 miles. However, users should also pay attention to symptoms of ignition system problems and have their vehicles checked when they notice any signs of trouble.
Q4: What is the difference between an ignition coil and a spark plug?
A4: An ignition coil is a component of the ignition system that transforms low voltage from the battery into high voltage to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine's cylinders. A spark plug receives this high voltage from the ignition coil and creates a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
Q5: What should vehicle owners do when they experience ignition problems?
A5: Vehicle owners should not ignore ignition problems, as they can worsen and lead to more significant issues. They should have their vehicles checked by a professional mechanic as soon as they notice any signs of trouble from igniter parts.