(6025 products available)








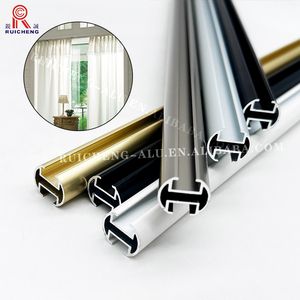




































































































































































































A hollow rail is a type of rail track that is quite different from the standard rail track design. Instead of a solid rectangular bar, it has a square or rectangular tube with rails on the outside. The inside of the tube is not solid and may have a web or be partially filled with concrete. There are several types of hollow rails including:
Hollow square rail
This is a type of hollow rail with a square cross-section. It is used in various applications such as construction and machinery. The main feature of this rail is its square shape, which provides stability and support in different situations.
Hollow rectangular rail
This is a type of hollow rail with a rectangular cross-section. It is commonly used in various industries, such as construction, manufacturing, and transportation. The rectangular shape and dimensions of this rail make it suitable for applications requiring strength, durability, and precise alignment.
Pre-stressed concrete hollow rail
This is a type of hollow rail that uses pre-stressed concrete technology to enhance its performance and durability. The pre-stressed concrete allows for better load distribution and resistance to cracking. This rail is commonly used in high-speed railways and heavy freight transportation.
Steel hollow rail
This is a type of hollow rail made from steel material. Steel is a commonly used material for making hollow rails because it offers strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. Steel hollow rails are used in various applications, such as construction, transportation, and industrial settings, where robustness and reliability are essential.
Aluminum hollow rail
This is a type of hollow rail made from aluminum material. Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant material, making it suitable for applications where weight reduction and resistance to rust or corrosion are desired. Aluminum hollow rails are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, where lightweight and durability are essential.
Each type of hollow rail has specifications that fit its use and design. Nevertheless, there are some general specifications to consider when buying these products.
Size
The size of the hollow rail affects its strength and ability to withstand loads. The size can also affect the weight of the rail. Hollow rails come in different sizes. This includes height and flange thickness.
Length
The length of the hollow rail depends on the application and transportation requirements. For instance, shipping long rails may be difficult. Therefore, buyers may ask for hollow rails cut into sections of manageable length.
Steel Grade
The steel grade determines the strength of the hollow rail. This includes the hardness and strength of the material. Hollow rails are made of high-strength steel. This makes them suitable for applications that require strength and durability.
Weight
The weight of the hollow rail can be a consideration in some applications. For instance, lifting and installation can be difficult with heavy hollow rails. On the other hand, the weight can be a benefit in applications where additional stability and strength is required.
Corrosion Resistance
Some hollow rails have coatings to make them resistant to corrosion. For example, galvanized hollow rails are coated with zinc to protect them from rust. These coatings increase the lifespan of the rail in applications where it is exposed to harsh elements or corrosive environments.
Flatbed Thickness
The flatbed thickness is vital for applications where mounting or installing equipment is required. A thick flatbed provides a sturdy surface for mounting, while a thin flatbed may be sufficient for other applications.
All the specifications of the hollow rail affect its performance in various applications. Therefore, buyers should consider the specifications that suit their needs.
Like all other equipment, properly maintaining the hollow rail is important. This ensures that it performs well and has a long lifespan. Here are some maintenance tips:
1. Regular Inspection
Users should regularly inspect the hollow rail for damage, wear, and signs of trouble. The earlier one notices an issue, the easier it is to fix it before it escalates into a bigger problem. The inspection should look for corrosion, cracks, and bending.
2. Cleaning
One should keep the hollow rail and the fittings clean. This prevents the accumulation of dust, grime, and dirt. This also reduces the risk of corrosion. A soft cloth, mild soap, and water are sufficient for cleaning the hollow rail.
3. Lubrication
The moving parts of the fittings and hardware of the hollow rail should be lubricated. This reduces friction, prevents wear and tear, and ensures smooth operation.
4. Tightening
The fittings and fasteners should be checked regularly and tightened if necessary. Loose fittings can cause instability and increase the risk of accidents.
5. Replacement
Worn-out or damaged components should be replaced immediately. This maintains the integrity and safety of the hollow rail.
When sourcing hollow rails, consider the following factors to ensure the best fit for customers' needs:
Application
What is the purpose of the hollow rail? Different applications may require specific sizes, shapes, and materials to suit various environments and load capacities.
Material
Hollow rails are produced using various materials. Buyers must consider the advantages and disadvantages of each material. For instance, steel is strong and durable, while aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
Size and dimension
Buyers should consider the size and dimension of the hollow rail to suit their application needs. This includes the wall thickness, height, length, and width of the rail. A customer requiring a rail for a passenger train will specify different dimensions from one sourced for a light train service.
Finish and treatment
Consider the finish and treatment of the hollow rail. Some have protective coatings that help them withstand corrosion and harsh environments. Additionally, treatment processes like tempering or annealing can improve the strength and durability of the rail.
Load capacity
Buyers should consider the load capacity and the strength of the hollow rail to support the application without failure or deformation. This is crucial when sourcing for parts of industrial machinery.
Installation and maintenance
Buyers should consider the ease of installation and maintenance of the hollow rail. Some designs may require special tools or equipment. Additionally, choosing a rail that is easy to clean and maintain can reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Cost
Cost is an important factor when sourcing hollow rails. Buyers must find a balance between quality, performance, and budget. They should consider the long-term benefits and savings of a reliable and durable rail.
Customization
Are there any specific requirements for the hollow rail? If yes, buyers should consider the possibility of customization to suit their application needs. Some manufacturers offer customized profiles, lengths, and treatments.
Installing a hollow rail staircase is very simple. Manufacturers offer DIY kits with detailed instructions on how to install a hollow steel rail. Here are the general steps to follow when installing a DIY hollow rail.
1. Pick a Location
Choose where the handrail will be installed. If it’s a staircase, decide which side of the stairs the rail will be fixed.
2. Prepare the Tools and Materials
Users should unpack the handrail kit and lay out all the components. Read through the installation manual and prepare all the tools that will be needed for the project.
3. Mark the Rail Placement
Use a pencil and measuring tape to mark where the brackets will be fixed. The brackets should be fixed at a reasonable distance to ensure the handrail is sturdy.
4. Drill the Holes
Use a power drill to make holes in the wall or the wooden frame where the brackets will be fixed. The size of the holes will depend on the type of screws provided in the kit.
5. Fix the Brackets
Use a screwdriver to fix the brackets on the drilled holes. Ensure they are tightly fixed and aligned.
6. Attach the Handrail to the Brackets
Once the brackets are fixed, users should attach the hollow rail to the brackets. Depending on the design of the handrail, it might be attached using screws or bolts.
7. Install the End Caps
Seal the ends of the handrail with end caps. This will improve the look of the rail and prevent users from injuring themselves on the sharp edges of the rail.
8. Test the Handrail
After completing the installation, test the handrail to ensure it is sturdy and secure. Give it a few shakes to confirm it doesn’t move.
9. Clean Up
Pick up any debris from the installation process. Dispose of any packaging materials and clean the handrail.
Q1: What does the term 'hollow rail' mean?
A1: A hollow rail is simply a train or tram track that is made with steel and has a hollow rectangular shape. The design is great for keeping the rail strong and for minimizing wear and tear.
Q2: What are the benefits of hollow rail compared to traditional rail tracks?
A2: Hollow rails have a number of advantages. For starters, they need less maintenance than traditional rails. Plus, the trains can run on them faster and smoother. Because of all these benefits, the lifespan of wheels and tracks increases, which in turn boosts profitability.
Q3: What is the difference between the inner rail and outer rail in hollow rail systems?
A3: The difference is just the same as the first and second face of the rail. The first and second sides of the rail are always more or less the same. In most cases, they are all aligned. The hollow rectangular rail has its inner side (the inner face of the rail) and the outer side (the outer face of the rail).
Q4: What are the first and second faces of a hollow rail?
A4: The first and second faces of a hollow rail are the same as the first and second sides. There is nothing new in the first and second faces of a hollow rail. They are always more or less the same and aligned. If they are not aligned, it will be a problem for the trains and tram to run on them.