(442 products available)







































































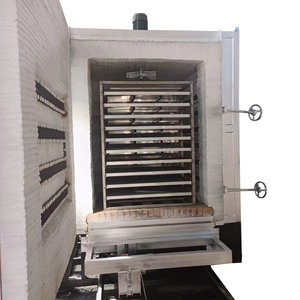

















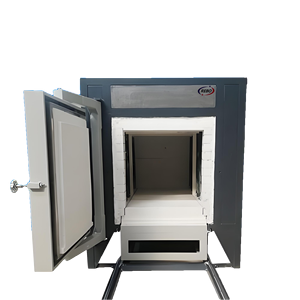















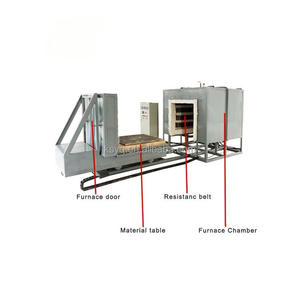















































































Hearth type furnaces are industrial heating equipment that offer a wide variety of features and options. The most common division method is according to the heating source used. The following types are thus segregated.
Hearth type electric furnaces
The electric hearth type furnace is a specialized industrial heating device that uses electric power as its sole source of heat. It is commonly utilized for heat-treating materials, such as metal parts and other substances, to achieve specific quality attributes and structural properties. This high-quality piece of equipment is used to improve the durability, hardness, and overall performance characteristics of the materials being processed. The versatility of electric power allows for precise control over the entire heat treatment process, such as tempering and cementation. By utilizing electric power as its main energy source, the electric hearth type furnace provides a stable, uniform, and efficient heating method. This ensures that the materials being treated undergo the heat treatment process evenly and thoroughly, leading to predictable and desirable results.
Gas-fired hearth furnaces
The gas-fired hearth furnace is an industrial heating device that uses natural gas or other gas fuels as its primary energy source. This type of furnace is widely applied in various industries for different heating needs, such as smelting, annealing, tempering, and heat treatment of metals and materials. The gas-fired hearth furnace offers a stable and controllable high-temperature environment that meets industrial production standards. This enables businesses to achieve more efficient and consistent manufacturing processes. The design of the gas-fired hearth furnace also emphasizes energy efficiency and environmental protection, thereby reducing the impact on the external environment during use.
Hearth type furnaces with auxiliary equipment
The hearth type furnace with auxiliary facilities is an all-encompassing industrial heat treatment device that, besides the primary heat treatment component, also incorporates auxiliary facilities for the entire production line. These auxiliary facilities may comprise loading and unloading mechanisms, quenching and cooling systems, dust removal and exhaust treatment units, control systems, and more. The combination of the hearth type furnace and auxiliary facilities may fulfill the needs of different industries and production procedures, thus enhancing production efficiency and automation levels. Simultaneously, the integration of auxiliary facilities enables a more complete solution for industrial processes, thereby guaranteeing the quality and stability of the product. The heating type furnace with auxiliary facilities possess great versatility and customizability and can be tailored to satisfy specific customer requirements and industry standards.
Hearth furnaces are used in the metallurgical industries, including ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy. This is the main application area in which the furnaces are used. Besides the metallurgy industries, the following areas are also applicable to hearth type furnaces.
Manufacturing industries
Hearth furnaces are widely used in metal manufacturing industries for different purposes, including smelting, casting, and heat treatment of the metals.
Construction industries
The construction industries make use of the hearth type furnaces for the purpose of casting various construction components, such as pipes, valves, and other critical structural.
Automotive and Aerospace industries
Hearth furnaces are used in the automotive industry for titanium and aluminum melting. Likewise, in the aerospace industries, they are used for alloy materials. The materials are precisely controlled using the atmosphere and temperature for the furnace's quality to meet various industry standards.
Tool and Die Making
Hearth type furnaces are also used in die making. They are used to heat the tool steel and other materials to high temperatures for the purpose of reaching the desired mechanical properties.
Energy production
In the energy production sector, the furnaces are often used for the treatment of energy metals like the production of solar cells and photovoltaic panels, among others.
When selecting a hearth type furnace, buyers should consider the purpose for which the furnace is used. Different industries and applications have varying requirements when it comes to heating processes, furnace designs, and capacity.
For instance, industrial sectors such as metallurgy, ceramics, and chemical processing typically opt for high-capacity commercial furnaces due to the large volume of materials they need to combust. Conversely, smaller-scale operations or residential needs may be adequately served by low-capacity or even portable models.
Additionally, it's crucial to consider the intended use of the combusted materials. Some industries may require the use of specific types of hearth furnaces to achieve particular product qualities or specifications.
The efficiency of a furnace's heating method can significantly impact production speeds and operating expenses. Many industries prioritize the use of electric furnaces because they offer faster heating times, leading to higher production rates. However, electric furnace costs can be higher than those of oil or natural gas-powered furnaces, which may influence a company's decision to use an electric furnace over other options.
Ultimately, it's essential to conduct a thorough analysis of an industry's needs, including required production speeds, combustion material types, and the chosen heating method's cost.
Q1: How are hearth furnaces different from pit furnaces?
A1: Both the types are similar, but the latter doesn't have a horizontal charge. Also, the heating in pit types may not be direct.
Q2: Are all industrial hearth furnaces open to the atmosphere?
A2: No, many furnaces are closed to serve specific applications like the heat treatment of steel.
Q3: Why are industrial hearth furnaces being replaced by other designs?
A3: The large area of ground they occupy and the high fuel costs have made many industries shift to vertical furnaces.