(1640 products available)








































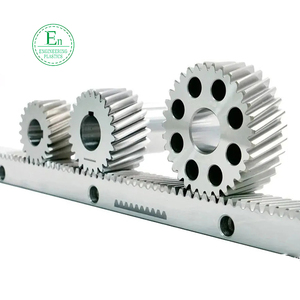














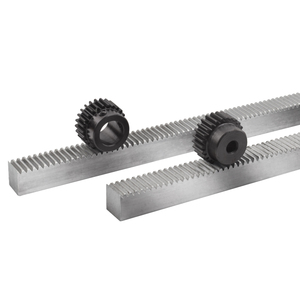












































































































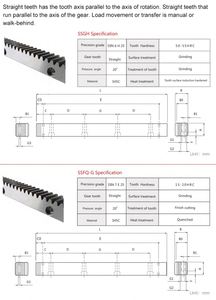
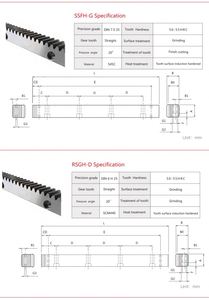






































Helical gears are analogous to how other gears are made, except that the teeth are cut at an angle to the axis of the gear. Stock helical gears can be found in two main types: single helical gear and double helical gear.
Single helical gear module:
An industrial gear with slanted teeth is cut into the gear wheel. The teeth are positioned in a way that allows them to mesh smoothly with other gear teeth. The single helical gear is similar to the helical gear, but it only features straight teeth. The gears are designed to engage progressively and smoothly, allowing load distribution across multiple gear teeth.
Double helical gear module:
It consists of two mirror-image helical gears positioned adjacent to each other, creating a V-shape. They are also known as herringbone gears. The load distribution is even better, and the helical angle helps eliminate the axial thrust that tends to occur in helical gears. However, double helical gears are more expensive and heavier than their single counterparts.
Other helical gears are made depending on the needs of different industries.
Straight cut helical gear:
The straight cut helical gear has a tooth design like the helical gear, with a notable difference being that the teeth are cut straight. Although the teeth design is similar to the helical gear, this gear design tends to have a shallow tooth profile. It is commonly used in low horsepower applications where noise is not a concern.
Cut helical gear:
An involute tooth profile matches gears commonly used in high horsepower gear applications. It tends to have a wider tooth base and is cut at an angle to allow for better load distribution. It's also used in applications where noise is not ideal, such as vehicles with differentials and industrial gear reduction equipment.
Bevel helical gear:
Spur gears are parallel to the shaft. Bevel gears are angled to the shaft, typically 90 degrees. The helical bevel gear combines helical and spur gear features and is designed with an angled tooth that can mesh with other gear teeth.
The specifications of helical gear modules largely depend on the specific applications and the needs of the customers. The following are key specifications that business buyers should know about helical gear modules before purchasing them:
Materials
Usually, helical gear modules are made from strong materials, such as nylon, carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Different materials have different features. For instance, carbon steel has high strength and durability, which makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion, which makes it ideal for use in harsh environmental conditions. This will enable business buyers to select suitable gear modules according to different application needs.
Shaft
Shaft refers to the diameter and length of the gear module's output shaft. It plays an integral part in connecting the gear module to other components in a system. Selecting an appropriate gear module with a matching output shaft can ensure solid connections and smooth transmission.
Module
The module refers to the ratio of tooth size to gear distance. It is a critical parameter that determines the size and spacing of gear teeth. Different applications may require different-sized gear teeth to achieve the desired transmission ratio and capacity. This allows business buyers to choose the right gear module according to specific use cases.
Tooth Amount and Profile
Helical gears are composed of teeth that work together to achieve transmission. The number of teeth and tooth shapes can affect the transmission efficiency and noise of the gear module. For example, more teeth can provide a more continuous and smooth transmission, while the tooth shape can affect the friction and engagement between the gears. Consequently, these will enable business buyers to select the gear module that offers the optimum transmission performance according to different applications.
Load Capacity
A helical gear module's load capacity denotes the largest load it can handle throughout its operation. It is typically affected by the gear's material, dimensions, and tooth profile. Business buyers can choose gears with appropriate load capacities based on usage scenarios to ensure equipment's stability and reliability.
In a word, the specifications of helical gear modules are diverse and flexible to meet various application needs. Meanwhile, proper maintenance is of great importance to helical gear modules to keep them in good working condition and extend their service lives. Here are some regular maintenance methods:
Regular inspection
Users can check the helical gear modules regularly to look for signs of damage, such as wear, deformation, or breakage of the gear teeth. They also need to examine the connections and alignments to ensure that they are in good working condition. If problems are found, users should address them promptly to avoid further damage.
Lubrication management
The helical gear module's smooth operation and wear resistance rely heavily on lubrication. Users should regularly add lubricants and select appropriate lubricants per the gear module's material and working environment. They should ensure that the lubricants are clean and free of contaminants to protect the gear module.
Cleanliness
To maintain the helical gear module's efficiency and longevity, users should keep it clean. They should remove dirt, dust, and abraded materials from the gear module with professional cleaning agents and tools. Additionally, they should keep the surrounding environment clean to reduce pollution and damage to the gear module.
Temperature control
Operating at the appropriate temperature range is vital for the normal operation of helical gear modules and longevity. Therefore, users should monitor the temperature during use and take cooling or heating measures as required to keep the gear module away from high or low-temperature damage.
Record keeping and analysis
Users can keep records of the usage status of the helical gear module, such as operating loads, temperatures, and abnormal performances, and regularly analyze the data. This can help identify potential problems early and enable users to optimize maintenance and management strategies.
The helical gear module is ideal for high-load and high-speed driving scenarios because its teeth are slanted, making gradual contact along a slope between the teeth. The following are typical application scenarios for helical gear modules.
Machinery industry
The helical gear module transfers high torque and power in mechanical machines. It is commonly used in mechanical machines like lathes, planers, and milling machines that cut metal. Besides, the gear module is found in assembly machines, gear cutting machines, and transport conveyor belts. In the mechanical industry, modules are also found in reducers, speed changers, and chain-driven devices. The gear module helps change motor speed while rotating an electric motor at high speed.
Automobile industry
Automobile cars use helical gears in different parts. An example is the gear of a car that rotates the shaft powerfully. The gear module rotates less in number but at high speed to transfer high twisting power to the car wheels. Car transmissions also have helical gears. This includes the car differential, which distributes power to the four wheels. Other places in vehicles where the gear module is found include the gearbox, windscreen wiper motor gearbox, and the electric motor gearbox.
Heavy industries
Industries that work with heavy machines prefer using helical gear modules because they can manage and sustain high-load weights. An example is the mining industry, which uses crushing and sieving machines. The gear module manages the high loads of crushing stones and the twisting forces of heavy-duty motors. Other helical gear machine industry applications include wind power generation, metallurgy, construction, marine, and water conservancy industries.
Robotics
Robotics uses helical gear modules to reduce motor speed and increase torque. Robotics industries use helical gears to support weight, control motion, and increase force in robotic arms, robot joints, and planetary gearboxes.
Transportation
Transportation vehicles like trains, motorcycles, and electric bikes use the gear module inside the transmission boxes. It's also used in the trains' power transmission shafts. The gear module transmits torque efficiently, allowing smooth motion and optimal bike power.
Office and household appliances
Some appliances at home and in the office use the gear module. An example is a vacuum cleaner that has to produce strong suction. Other appliances include washing machines, microwave ovens, blender and printer machines.
Load Capacity:
For proper functioning, selecting a suitable load-bearing capacity helical gear module is crucial. Analyze the expected torque and weight of the machine. Choose gear modules with load capacities that exceed these figures to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature wear or failure.
Material:
The material used for helical gear modules can significantly impact their performance and durability. Metals such as steel and cast iron are commonly used due to their excellent strength and load-bearing capabilities. For applications requiring lightweight and high-strength materials, consider using polymer-based helical gear modules. Each material has advantages and disadvantages, so choose the one that best suits the specific application requirements.
Axis Alignment:
Helical gears function most efficiently when their axes are perfectly aligned. Misalignment can cause uneven tooth wear, increased friction, and higher energy consumption. During installation, take the necessary precautions to ensure that the gear-helical axes are well-aligned. Make adjustments to the mounting brackets or supports until the desired alignment is achieved. Regularly inspect the alignment and make any necessary adjustments to maintain optimal axis alignment for long-term performance and reliability.
Coating:
Helical gear modules are often coated with a protective layer to improve their durability and lifespan. Common coatings include anodizing, powder coating, and electrophoretic coating. Anodizing provides excellent scratch resistance while allowing heat dissipation. Powder coating offers a thicker, chip-resistant layer but may limit heat transfer. Electrophoretic coatings are thinner and smoother, providing better lubricity and reducing friction between moving parts. Consider the specific application requirements and choose the suitable coating to enhance the helical gear module's performance and longevity.
Q1: How to determine the gear module?
A1: The gear module can be determined by measuring the pitch diameter and the number of teeth. Firstly, the pitch diameter of the gear is calculated. It is the hypothetical diameter at which the gear teeth effectively engage with the teeth of another gear. The pitch diameter can be calculated from the following equation:Pitch Diameter = Module x Number of Teeth/2. Then, the gear module can be derived by dividing the pitch diameter by the number of teeth.
Q2: What are the advantages of helical gears?
A2: Helical gears offer several advantages. They can smoothly transmit power between non-parallel shafts. This feature makes them suitable for complex machinery that requires high power transmission. Helical gears also perform well at high speeds and can reduce noise levels. Additionally, they are strong and durable, which improves the overall performance of machines.
Q3: What materials are helical gears made of?
A3: Helical gears are commonly made of steel. Stainless steel helical gear modules are widely used in many applications to achieve high strength and prevent corrosion. Some applications require heavy-duty helical gears, so manufacturers use alloy steel to improve the gear's strength and durability. In addition to alloy steel for heavy-duty helical gears, plastic helical gears are also used modules to reduce weight and noise.