(4233 products available)



















































































































































































































These sheets can be classified into various types depending on material composition and fabrication technology.
Hot-dip galvanised sheets
This is the most widely used GC sheet as it is formed by dipping a thin steel sheet into molten zinc. This leads to a thick layer of corrosion-resistant coating. This provides long-lasting protection in outdoor-related applications and is widely used for roofing, cladding, and automotive parts.
Electro-galvanised sheets
These sheets are galvanised by having an electric current run through the solution containing zinc and the steel sheet. While the zinc coating is thinner, it provides adequate corrosion resistance for indoor applications like electrical appliances, and automotive components. These sheets are known for their smooth finish and better paint adhesion.
Galvalume sheets
These sheets are coated with a mixture of aluminium, zinc, and silicon. They offer superior corrosion protection compared to pure galvanised steel sheets. The alloy coating reduces the amount of heat absorbed by the sheet allowing it to have a longer service life. These types of sheets are widely used in roofing applications and telecommunications.
Features of GC Sheets
Corrosion resistance
The primary function of galvanisation is to protect the base metal from rust and corrosion. Zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, meaning it corrodes preferentially to protect underlying steel. This is why they are widely used in outdoor applications exposed to moisture and adverse environmental conditions, such as in coastal regions.
Durability and strength
Galvanisation also increases the mechanical strength of the sheets. This leads to a longer lifespan in many applications, with the coating providing an extra layer of protection during wear and tear due to scratches and dents. This increases longevity in the automotive industry, building constructions, and manufacturing.
Heat and thermal resistance
GC sheets can withstand high temperatures thanks to the thermal explainability of zinc. This property makes it especially useful in roofing sheets as they can endure sunlight, and extreme heat without degrading. They are also resistant to such elements as ozone and ultraviolet radiation.
Used in roofing and building
GC sheets are mostly used in the building and construction industry to make roofing sheets, walls, and other structural components. This is a result of their corrosion resistance and durability. They are widely used for roofing in residences, industrial, and commercial structures, withstanding adverse weather conditions and providing long-lasting protection.
Used in automobile manufacturing
Another area of application is the automotive industry. This is where GC sheets are used to make inner bodies, doors, and other external panels. Zinc coatings provide adequate protection against rust and corrosion, ensuring the longevity of automotive components that are often exposed to moisture and water.
Manufacturing of electrical appliances
Galvanised coats are also applied to steel sheets to manufacture electrical appliances and other consumer products. Washing machines, refrigerators, and other appliances contain GC sheets to prevent internal and external rusting. In this case, Electro-galvanised sheets are majorly applied due to their smooth finish and superior paint adhesion.
Industrial machinery and equipment
GC sheets are also used to construct ducts, conveyors, and storage tanks in industrial machinery and equipment. Corrosion resistance helps with maintenance reduction and increases the longevity of parts exposed to chemicals or humid environments. This leads to a reduced cost of operations.
Manufacturing of packaging materials
Galvanised sheets are used to manufacture tin plates, which are later transformed into cans and other containers for food, chemicals, and beverages. Galvanisation helps in providing the containers with resistance to rust and reaction with contents. Cans are widely used in packaging liquids, food, and consumer goods.
Type of galvanisation
Since there are two main types of galvanisation: electro-galvanised and hot-dip galvanised select the one that meets the intended application. If needed for indoor applications like machinery parts and appliances, electro-galvanised sheets can be better since they have a smooth finish. However, if the sheets are to be used outdoors and require more robust corrosion resistance, the hot-dip galvanised is much better.
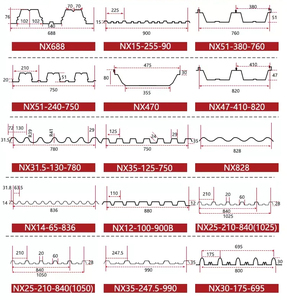
Thickness of galvanised coating
The thickness of the galvanised coating affects corrosion resistance. Tighter coatings are better for high-humidity areas, marine environments, or situations where long-term outdoor exposure is expected. Shallow coatings may be suitable for indoor applications. Consider the sheet thickness to ensure the required durability is met by the coating.
Steel sheet gauge
The choice of gauge (thickness) of the base steel sheet depends on the mechanical requirements and structural applications. Lower-gauge numbers mean thicker sheets which are better for heavy duties such as buildings, roofing, or automotive components. Higher gauge numbers are adequate in light-duty applications where flexibility is required. The required thickness of the galvanised coating is also dependent on the application.
Mechanical bond and adhesion
Some applications require painting or coating over the galvanised sheet. In these cases, selecting a sheet that has a better mechanical bond with the paint and superior adhesion is essential. Galvanised iron sheets have superior paint adhesion due to the electrolyte that is created during galvanisation.
International quality standards
So as to ensure uniform quality select galvanised sheets that meet recognised standards like ASTM or ISO certifications. Such standards ensure that the sheets conform to specifications in galvanisation and mechanical properties which affect the performance of the sheets. Moreover, the seller must provide reliable test certificates for zinc coating thickness and tensile strength.
A1: Hot dip galvanisation offers superior corrosion resistance and is better for outdoor use. On the other hand, electro-galvanised provides a smoother finish and is suited for indoor applications.
A2: They are made to meet international specifications such as ASTM A653 for exposure and ASTM A791 for corrosion resistance.
A3: They resist rust, provide added strength, and endure weather conditions. They are also resistant to ozone and UV radiation and can withstand up to 40 years without degrading.
A4: A zinc layer is provided that protects the sheets from moisture and chemicals. The same sacrificial anode principle applies to the sheets.
A5: Yes, this is because zinc coating prevents thermal expansion and protects the sheets from UV radiation. They also resist heat, snow, and ice.