(2268 products available)
















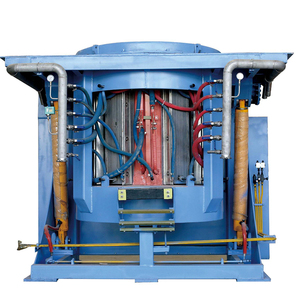








































































































































































































A hot blast stove is an essential part of a blast furnace. It is used to heat the air blast that is sent to the blast furnace for iron ore reduction to produce iron. Therefore, it can also be considered a compartment that stores heat in the blast furnace.
In a hot blast stove, the air blast is heated by the hot gases that come from the combustion of fuel in the cupola. It is constructed with two main parts - the vertical part or column, and the dome or the horizontal part that looks like a dome on top. The hot blast stoves can be of two types based on their design: linear flow hot blast stoves and cross flow hot blast stoves.
Another way to categorize the hot blast stove is based on the materials it is made up of. There are two common types of hot blast stoves: ceramic hot blast stoves and steel hot blast stoves.
Material
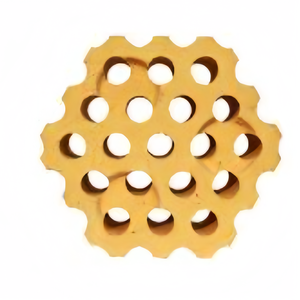
The refractory material used in hot blast stoves has a high melting point. It can resist heat without deteriorating or deforming. Common materials include high-alumina bricks, silica bricks, and refractory ceramics. High-alumina bricks have an Al2O3 content above 48%. They possess high-temperature resistance, thermal stability, and low expansion coefficient, making them suitable for hot blast stove linings. Silica bricks contain over 90% SiO2 and are used in areas where high heat is encountered. Their high melting point and low thermal conductivity help retain heat. Refractory ceramics can also be used for blast furnace hot blast stoves. They may include materials like cordierite-mullite ceramics, which exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance and stability at high temperatures.
Pressure
Hot blast stoves operate at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 0.3 MPa, a key factor affecting their efficiency. Blast furnace pressure, which refers the force exerted per unit area, plays a critical role in controlling the volume and temperature of the hot air injected into the blast furnace during the hot blast stoves' operation. Stoves with pressures in this range ensure a constant supply of high-temperature airflow to the blast furnace, promoting optimal combustion and reducing the formation of coke in the ironmaking process. By regulating this pressure, it is possible to stabilize the reaction conditions within the blast furnace thereby enhancing the yield of pig iron while simultaneously minimizing the consumption of raw materials.
Heating system
Hot blast stoves commonly use natural gas as their primary fuel, along with other options such as heavy oil, diesel oil, and light oil. The choice of fuel depends on factors such as availability, cost, and specific operational requirements. In addition to these conventional fuels, there is a growing trend toward utilizing waste heat from gas engines and gas turbines as indirect heating sources for hot blast stoves. This shift not only diversifies the energy inputs for the stoves but also contributes to sustainable development by making use of waste heat energy.
Structure
A hot blast stove consists of several key components, including the combustion chamber, insulation layer, flue gas duct, and blast main. Each part plays a specific role in ensuring efficient heat generation and transfer. The hot blast stove also has a dome at the top and a bottom outlet. The dome serves as a cover for the entire stove, while the bottom outlet provides a passage for hot air to be released into the hot blast main.
In addition to the proper selection of refractory materials, regular inspections and timely repairs of the stoves are also necessary to ensure their long-term use. Attention should be paid to the quality of the blast furnace hot blast stove linings, as poor-quality materials may cause great harm. For example, some linings are difficult to remove due to their high adhesiveness. In such cases, it is better to replace them with alternative linings that can be easily and conveniently removed.
Industrial hot blast stoves are an integral part of processes that require a large amount of heat. Here are some industries that have used or will effectively use the hot blast stove.
The iron and steel industry uses the hot blast stove. The hot blast stove heats the air used in the blast furnace to about 1,000 degrees Celsius. This is a great way to increase the furnace's output and efficiency while cutting operating costs.
The non-ferrous metallurgy industry also uses hot blast stoves. This is done to process copper, zinc, lead, nickel, tin, titanium, and aluminum. These materials make up a large percentage of the metals that industries and manufacturers use. The industry has decided to make use of hot blast stoves to improve things like productivity, extraction rates, and cost-effectiveness when processing these metals.
The hot blast stove has also found a great use in the ceramics industry. It is used to fire ceramic products like pottery, porcelain, tiles, and sanitary ware. The hot blast stove's ability to provide a constant and high temperature is very great for achieving the optimal strength and durability of ceramic products.
Blast hot stoves are also used in the glass industry. Glass containers, flat, and fiberglass products are made up of good quality glass. This achieves good transparency and stability. The use of the hot blast stove provides the steady heat needed for this. In the end, this result is excellent quality glass products.
The cement industry also uses hot blast stoves. They are used for the calcination of limestone and clinker production. The hot blast stove provides the high temperatures needed for these processes. It also helps boost the efficiency of cement ovens.
The chemical industry makes use of hot blast stoves for some chemical processes that need high and constant heat. Examples are the production of fertilizers, petrochemicals, and specialized chemicals. The hot blast stove provides the steady and high temperature that's often needed for chemical reactions, thus promoting the chemical factories' productivity and yield.
In the paper industry, hot blast stoves are used to produce pulp. The stoves supply the heat that is needed for the cooking and bleaching of wood fiber. Hot blast stoves improve the output rates of pulp and also reduce the cost of production.
Every industry that requires a constant and high amount of heat ends up making use of the hot blast stove. This includes the rubber industry, the food industry, and the textile industry, among others.
When choosing a blast furnace hot blast stove for sale, consider furnaces that are made with quality materials so that they last for several years. Typically, these stoves are made with refractory material both in the outer and inner walls of the hot blast stove. This material has great resistance to high temperatures. It is able to retain as much heat as possible and is built to last. In the end, this will help reduce operational costs.
It is important to note that the cost of the hot blast stove does not correlate to the performance. When choosing a hot blast furnace, compare the prices and efficiency of different stoves. A more expensive hot blast stove could have an improved design that will offer better energy efficiency, further reducing the overall operating costs.
Choose a type of hot blast stove that fits the needs of the business. Classical hot blast stoves or semi-dry hot blast stoves are suitable for industries that use a lot of coke. On the other hand, regenerative hot blast stoves are ideal for firms looking to improve their energy usage.
When selecting a hot blast stove, pay attention to the lining. Different hot blast stoves have linings that correspond to specific applications. Those with acidic linings are mostly used in ferrous and non-ferrous industries. Basic linings, on the other hand, are used in industries that handle alkaline materials. Choose a lining that matches the needs of the industry to achieve better results.
It's also important to choose a hot blast stove that has a clear setup and functionality. Complicated operating techniques will require a large workforce with expertise who will demand higher salaries. This will further increase the overall production costs. If the working staff is small, the furnace's insensitivity to the mass and through put is better.
Choose a hot blast furnace supplier that offers great customer support. They should provide installation services as well as maintenance and after-sales services. A good supplier will help businesses avoid costly mistakes that could shut down production lines.
Q: What is the connection between a furnace hot blast stove and a furnace heating element?
A: A furnace heating element is one of several ways to heat a furnace. A furnace blast stove is another way to achieve this purpose.
Q: What are some of the experiments being carried out on hot blast stoves?
A: There have been several attempts to eliminate hot blast stoves entirely by designing furnaces that utilize the combustion of fuel directly in the iron ore to reduce it, thereby eliminating the need for additional hot air blasts. However, such endeavors have yet to be successful on a large commercial scale.
Q: Do all furnaces have blast stoves?
A: No. Some modern blast furnaces use hot blast stoves called hot blast generators that achieve the same purpose more efficiently and effectively. Such stoves are usually referred to as waste heat recovery units.
Q: What are the modern alternatives to the hot blast furnace?
A: The vertical shaft furnace is probably the most noteworthy alternative to the blast furnace. It has a higher production capacity and is more environmentally friendly than its counterpart, the blast furnace.