(28928 products available)









































































































































































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship




















A detective GPS tracker has various types, each designed for a specific purpose. The following are some of the common types:
Real-Time GPS Trackers
These devices allow users to track the location of an asset in real time. They update the location information at regular intervals, usually every few seconds or minutes, depending on the settings. For example, a detective can use these devices to track a suspect's vehicle movement in real time.
GPS Data Loggers
These devices keep track of the location information but do not communicate that information in real time. Instead, they periodically record the location data and store it in the device's memory. Users can later download the data to a computer or other devices to analyze the tracking information. For example, a GPS data logger can be used to track the location of a delivery truck during a certain period.
Active GPS Trackers
These devices continuously monitor the location of an asset and send updates to a central system or to the user's device. They have built-in communication capabilities, such as cellular, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth, to transmit location data. Active GPS trackers are often used for fleet tracking, personal tracking, and asset tracking. For example, a fleet management company can use active GPS trackers to monitor the location and movement of its vehicles in real time.
Passive GPS Trackers
These devices record location data but do not transmit it. They are designed to capture and store the data internally for later retrieval. Users must connect to the tracker using a computer or other devices to download the stored data. Passive GPS trackers are often used in applications where real-time tracking is not essential but where tracking data must be collected over time.
Personal GPS Trackers
These devices are small and portable, often worn by individuals or carried in personal belongings. They provide tracking services for personal safety, such as tracking children, the elderly, or individuals in emergencies. Personal GPS trackers can be active or reactive, depending on the specific needs and applications. For example, a personal GPS tracker can help parents monitor their children's whereabouts or track a pet's location.
Fleet GPS Trackers
These devices are integrated into vehicles to track their location and movement in real time. Fleet GPS trackers are active and provide information on traffic, vehicle speed, and other parameters. Users can use the data to optimize fleet management, monitor driver behavior, and improve operational efficiency. For example, a logistics company can use fleet GPS trackers to track delivery vehicles and ensure timely deliveries.
Frequency and band:
GPS trackers use mobile networks to transmit data. They use a particular frequency band and support a specific network frequency. For example, some trackers work on the 2G frequency band (850/900/1800 MHz), while others support 4G LTE (700/850/1700/1900 MHz) with a 2G fallback. This allows the device to work on a wider range of mobile networks. The supported frequency and band affect the compatibility of the GPS tracker with mobile networks.
GPS accuracy:
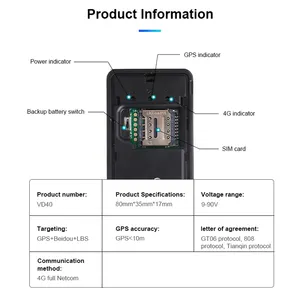
GPS accuracy refers to the precision of location data provided by a GPS tracker. High accuracy means the device can determine the user's location with great detail. For example, it can pinpoint the location within a few meters. This is important for applications where precise tracking is required, such as monitoring valuable assets or tracking the movements of children. Lower accuracy, on the other hand, can provide a broader estimate of the location. In this case, the device may indicate the user is in a specific area or neighborhood, but the precision is not as fine-tuned. Lower accuracy may be sufficient for use cases where exact location data is not critical.
Battery life:
The battery life of a GPS tracker is determined by its size and the frequency of location updates. These devices come in various sizes, from small ones that can be hidden in a shoe to larger ones that may be the size of a mobile phone. Smaller trackers are designed to be compact and consume less power, resulting in longer battery life. Additionally, the frequency of location updates affects battery performance. If the tracker updates the location frequently, it requires more energy, leading to shorter battery life. Conversely, if the updates are less frequent, the battery will last longer. For example, a small GPS tracker with infrequent location updates may last for weeks or even months on a single charge. In contrast, a larger tracker with frequent updates may require recharging every few days.
Waterproof and dustproof ratings:
Waterproof and dustproof ratings are important specifications for GPS trackers, especially for outdoor or rugged use. These ratings indicate the level of protection against water and dust ingress. They are measured using the Ingress Protection (IP) system. The IP system consists of two digits. The first digit measures the protection level against solid objects like dust, while the second digit measures the protection level against liquids like water. For example, an IP67 rating means the GPS tracker is completely dustproof and can be submerged in water up to 1 meter for 30 minutes without damage. Lower ratings, such as IP54, provide limited protection against dust and splashes from water. Users should choose appropriate waterproof and dustproof ratings based on the environment where the GPS tracker will be used.
Regular maintenance of GPS trackers is essential to ensure they continue to work properly and accurately track locations. Here are some tips for maintaining detective GPS trackers:
Choosing the right GPS tracker can be daunting because of the many options available in the market. Before making any decisions, consider these factors:
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to replace a GPS tracker:
Research
Find out the make and model of the existing GPS tracker. This information is important for getting a compatible replacement.
Purchase a Replacement
Buy a new GPS tracker that matches the old one in specifications. It should be from the same manufacturer or a comparable one.
Prepare the Vehicle
Turn off the vehicle's ignition and electrical systems. This will help avoid electrical shorts or damage to the car's electronics.
Remove the Old GPS Tracker
Follow the instructions for uninstalling the old GPS tracker. Typically, it is held in place with screws, adhesive, or a combination of both.
Connect the New GPS Tracker to the Vehicle
Follow the manufacturer's instructions for connecting the new GPS tracker to the vehicle. This may involve connecting to the vehicle's OBD-II port or wiring it to the electrical system.
Mount the New GPS Tracker
Find a suitable location for mounting the new GPS tracker. It should be a place where it can receive a clear signal from satellites and is not easily accessible to thieves. Common mounting locations are under the dashboard, near the windshield, or inside the center console.
Test the New GPS Tracker
Once the new tracker is installed, turn on the vehicle and ensure the GPS tracker works. Check its functionality by tracking the vehicle's location using a computer or smartphone.
Secure Wires and Components
Ensure all wires and components are secure and not interfering with the vehicle's operation. Use zip ties, electrical tape, or other appropriate methods to organize and secure the wires.
Dispose of the Old GPS Tracker
Follow local regulations for disposing of electronic waste. Do not throw away the old GPS tracker with regular household garbage.
Q1: How long does the battery of a detective GPS tracker last?
A1: The battery life of a detective GPS tracker depends on several factors, including the type of device, usage, and tracking frequency. Some trackers have a battery life of up to two weeks or more on standby. However, those with high tracking activity intervals have a shorter battery life.
Q2: Can a detective GPS tracker be used on pets?
A2: Yes! A detective GPS tracker can be used on pets. However, it is advisable to choose a lightweight tracker that is not cumbersome to the pet.
Q3: How accurate is a detective GPS tracker?
A3: Generally, the accuracy of a detective GPS tracker depends on various factors, such as the type of GPS technology used and environmental conditions. However, advanced GPS technology provides accurate tracking with an accuracy range of 5 to 10 meters.