(2622 products available)

































































































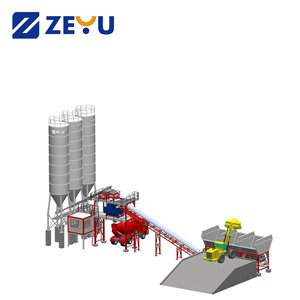















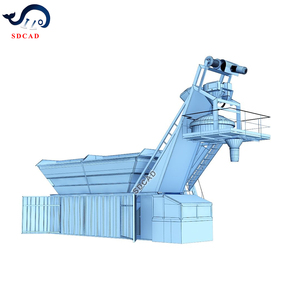
























































































A concrete recycling plant collects, processes, and sells recycled concrete for construction. It typically consists of a concrete crusher, screening equipment, magnetic separators, washing equipment, stockpiling systems, and sometimes, asphalt recycling plants. The concrete is first crushed by the cement crusher, which breaks it into smaller pieces. The different types of concrete recycling plants are as follows:
Cement and Aggregate Separation
This type of concrete recycling plant separates cement and aggregates using a combination of mechanical and water processes. The plant may use vibrating screens to separate smaller particles, while larger magnets may be employed to extract metallic parts. A wet process utilizes water for separation, and it can help to reduce airborne dust.
Refrigerated Water Separation Plants
A refrigerated water separation plant uses a closed-loop system to separate different components of crushed concrete. The system employs refrigeration to cool the water, thereby allowing for the effective separation of particles of varying sizes. This method not only reuses water in the process but also reduces the consumption of raw materials and minimizes waste generation.
Asphalt Concrete Recycling Plants
Asphalt concrete recycling plants process discarded asphalt concrete, which is commonly found in roads and pavements. These plants typically use crushed materials to recover asphalt binder and aggregates. The recovered materials can then be reused in the production of new asphalt concrete mixes, thereby reducing the demand for virgin materials and conserving natural resources.
Wet Concrete Recycling Plants
Wet concrete recycling plants collect and treat the water generated during the mixing and curing processes. These plants use techniques such as sedimentation, filtration, and separation to ensure that the water is suitable for reuse in the production of fresh concrete. By implementing wet recycling methods, these plants help to minimize water pollution and promote sustainable construction practices.
Crushed Concrete Transfer Stations
These transfer stations serve as collection points for crushed concrete, which is then transported to recycling facilities for further processing. By centralizing the collection of crushed concrete, these transfer stations aim to reduce transportation distances, decrease traffic congestion, and lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with construction waste disposal.
Mobile Concrete Recycling Units
Mobile concrete recycling units provide on-site recycling solutions for construction projects. These compact and portable units can be easily transported to different locations, allowing for the immediate processing of concrete waste directly at the construction site. By enabling real-time recycling, mobile units help to reduce transportation costs, minimize environmental impact, and promote sustainable construction practices.
The specification of concrete recycling plants can differ between models, but the following are the essentials.
Production capacity
The production capacity of a mobile concrete recycling plant indicates how much concrete waste it can process in a specific time frame, usually expressed in tons per hour. The higher the capacity, the more concrete waste it can handle efficiently. Businesses should choose a plant with a production capacity that matches the volume of concrete waste they generate. For example, a small construction site may opt for a plant with a capacity of 5-10 tons per hour, while a larger infrastructure project may require 20-30 tons per hour or more.
Processing technology
Concrete recycling plants use different processing technologies to crush and sort concrete waste. Some plants have stationary crushers, while others use mobile crushers. The technology used will determine the efficiency and effectiveness of the recycling process.
Size and weight
Concrete recycling plants come in different sizes and weights, depending on their capacity and technology. A smaller, mobile plant may measure around 10-15 meters in length, 3-4 meters in width, and 3-4 meters in height, weighing around 20-25 tons. Larger, stationary plants are more massive and take up more space. They may measure about 20-30 meters in length and 6-8 meters in width, with an average weight of 50-60 tons.
Power source
Concrete recycling plants use different power sources to operate. Most plants are powered by electricity and come with a specified voltage requirement. For instance, a plant may need a three-phase 400V power supply. Some plants have optional generator sets to provide flexibility.
Dust control
Dust control systems are important features in concrete recycling plants. Such systems prevent excessive dust from spreading during the crushing and sorting processes. The dust control features may include water sprinklers, water mist cannons, vacuum extraction systems, or bag filter units.
Proper maintenance is vital to keep the concrete recycling plant functioning well and ensure design life. Users can follow these maintenance tips:
Concrete recycling plants carry immense potential with a growing array of application scenarios.
Public Infrastructure Projects
Growing populations and urban congestion call for efficient land use rather than construction. Concrete recycling plants save local economies through cost-effective solutions. Infrastructure projects require massive volumes of concrete. Public works, which make up a sizable portion of concrete use, provide an easy application for recycled aggregate.
Road Construction and Repair
Roads constitute a sizable percentage of domestic infrastructure expenditure. Replacing the stones used for road maintenance, creation, or expansion with recycled concrete lowers costs and is ecologically responsible.
Landscaping and Gardening
Garden and landscaping projects frequently choose recycled concrete as decorative stones. Cheap and unique stone aggregates give a hint of luxury to everyday projects. Recycled concrete chips and stones beautify and support soil drainage functions.
Masonry Projects
Mortar and masonry projects provide an ideal field for recycled concrete. Large portions of recycled concrete form perfect backfills and drainage layers for masonry. The project utilizes recycled concrete soil drainage aggregates, thus lessening the total volume of waste utilized in the project.
Industrial Applications
Industrial processes create large volumes of concrete waste. Concrete recycling plants provide a local, low-cost solution through on-site concrete recycling. Factories save transportation costs and aggregate purchases through on-site recycling machines. Concrete reprocessing saves money and reduces the transportation carbon footprint.
Concrete Production Facilities
Production facilities require massive amounts of aggregate. Large-scale concrete recycling plants provide aggregate for new concrete production. Concrete recycling connects two previously separate industries. The concrete recycling plant feeds the cement production process.
Construction Material Supply Companies
Large volumes of concrete waste are an opportunity to create a new product. Concrete recycling plants can transform concrete into a new product. Construction material suppliers can distribute large volumes of concrete products.
Demolition Companies
Demolition projects are the source of much concrete waste. Concrete recycling plants located near demolition sites can process the waste quickly and cost-effectively. The close proximity reduces transportation costs and times. Urban areas with frequent demolition projects benefit the most.
Quarry Restoration Projects
Quarries seeking to restore disturbed land benefit from concrete recycling plants. The plant can process large volumes of concrete to restore quarried land. Land restoration projects require large volumes of aggregate. Concrete recycling reduces the need for new aggregate by transforming urban waste to restore rural land.
Business buyers seeking suitable concrete recycling plants for sale should look for a machine that offers a high-productivity rate and good ROI. Factors that influence the plant's productivity are its feeding system and crushing system configuration. In addition, the buyers should also look for the type of concrete the machine can handle. They should get concrete recycling plant samples and test how well they process different types of concrete.
Locate the suppliers' production lines. Buyers should identify the suppliers whose production lines are near their market demand. They should choose suppliers whose plants will help them meet their customers' demands. In addition, buyers should also check concrete recycling plants' automation levels. They should evaluate the machine's manual and automated tasks and decide on the required personnel. If the plant has a low level of automation, they might need to hire extra staff, increasing the operational cost.
Apart from the upfront cost of the recycling plant, buyers should also consider the operating cost to determine the overall yearly budget for the machine. The operating costs include electricity consumption, water usage , maintenance requirements, spare parts availability, and any licensing fees required to operate the plant. Negotiate the price with the suppliers, including the discounts on bulk orders and shipping costs. Calculate the entire cost to ensure a great ROI.
Finally, look for the concrete recycling plant's compliance with local environmental regulations. The plant must have an air pollution control system that minimizes harmful emissions and protects the environment. Establish a solid relationship with suppliers that offer great after-sales support and installation services. A good after-sales support can make the buyers' operations seamless and smooth.
Q1: What is the working process of a concrete recycling plant?
A1: The general working process of a concrete recycling plant is feeding, crushing, screening, separating, collecting, and discharging.
Q2: What types of concrete can be processed by a concrete recycling plant?
A2: Concrete recycling plants are designed to process various types of concrete waste, such as old concrete from demolished buildings, road repair concrete, and fresh concrete from leftover batches at construction sites.
Q3: What are the storage methods of the aggregates produced by the concrete recycling plant?
A3: The recycled aggregate can be stored in silos or the open air. Silo storage is suitable for small amounts of aggregates. Furthermore, using a silo will help keep materials secure and protected. On the contrary, open-air storage is suitable for huge amounts of aggregates.
Q4: What are the maintenance requirements for a concrete recycling plant?
A4: Concrete recycling plants require regular maintenance, such as lubrication, inspection, cleaning, and repair. The recycling plant's maintenance will prolong the lifespan and keep it running smoothly.