(20613 products available)































































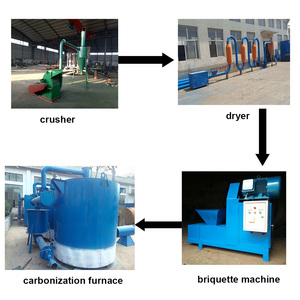
























































































































































A carbonization kiln, also known as a carbonization furnace or oven, is an industrial facility used to heat organic materials in the absence of oxygen. Different types of carbonization kilns are used globally, depending on material availability, demand, technological advancement, and budget constraints.
The traditional carbonization kiln is a round metal container with a layered bottom. It is an open-air production method that starts with lighting a fire beneath the kiln. When the wood is carbonized, charcoal is produced. An advantage of using the traditional carbonization kiln is that it can be easily built at a low cost. However, this type of kiln pollutes the air.
The lab-scale carbonization kiln is mostly made of metal. Organic materials such as biomass are heated until they are pyrolyzed inside the lab-scale carbonization lab kiln. The purpose of a lab-scale carbonization kiln is to study the characteristics of the material that will be produced after carbonization occurs. A disadvantage is that the amount of material that can be processed is limited.
The continuous carbonization furnace functions as an uninterrupted process by feeding raw material and discharging end products simultaneously. A big advantage of using this type of carbonization kiln is that it has a large production capacity, high level of automation, and efficiency. The temperature and pressure levels inside the kiln are also maintained. This type of carbonization kiln is suitable for industries that demand high product quantity and quality.
Modular carbonization kilns are designed for different carbonization methods like batch, continuous, or semi-continuous. They provide flexibility in production and can usually be tailored to specific requirements. Containerized carbonization kilns are transportable units suitable for small to medium-scale production. Standard containers house the kilns, making them ideal for remote site location or temporary operation at different locations.
The indirect-fired rotary carbonization kiln consists of an outer shell and a fixed furnace chamber. The inner paddle blades mix the materials. The materials will be heated and carbonized by the high-temperature hot air that flows inside the furnace chamber. An advantage of using this type of carbonization kiln is that the feedstock is carbonized uniformly inside the furnace chamber. There are no contaminations from the fuel inside the kiln.
Capaicty
The typical capacity of a carbonization kiln can vary widely depending on the design and intended use.
Income furnaces, for example, might handle anywhere from a small amount, like a few hundred pounds per batch, to big business-scale kilns that could process many thousands of pounds of input material each time they run.
This leading batch size affects how large the overall capacity is because it determines how much wood or other feedstock can fit in.
Operating temperature
Carbonization kilns need to get very hot - usually between around 400 and 800 degrees Celsius at least, but sometimes even higher - in order to break down the wood molecules.
Each kiln model has a different maximum temperature depending on its design, and also the materials used to build it. The higher the carbonization temperature, the more volatiles can escape from the wood and the richer the charcoal will be in carbon.
Heat source
Carbonization kilns have various ways of generating the heat needed for the chemical changes in wood to occur to produce charcoal. Some use electricity, while others burn gas, diesel fuel, or heavy oil. Other methods include letting sunlight heat the kiln directly or through solar panels, or using ambient atmosphere pressure combined with heat from other sources.
The key to ensuring the long life of a carbonizing kiln and preventing costly downtime from frequent breakdowns is regular maintenance and inspection.
Establish a routine schedule for carefully looking over the most important parts of the kiln that tend to wear out over time or break down often.
Pay special attention to the feeding system used to put in new wood and the discharging system for getting the finished charcoal out, since these are critical for operation day after day.
Also, routinely check the sealing, insulation, and pipe elements. Established airflow routes can be preserved by periodically replacing damaged seals and adjusting the insulation to ensure it remains properly spaced around the pipes, which need to be effectively cleaned of dirt buildup.
Because it's so important to carbonizing kilns' productivity and efficiency levels, users should do consistent maintenance on these key components as well as allow them to be utilized at their full capacity through proper operating techniques learned via training programs, ensuring systems serve Their intended function best while minimizing avoidable costs associated with regular repair necessities through preventative measures taken early on.
The primary application of a carbonization kiln is to produce charcoal from organic materials. However, the carbonization process itself has a number of applications in industrial production and research. Such applications require specialized carbonization kilns or furnaces designed for a specific material or use.
Raw materials:
Production capacity:
Consider the intended production capacity for carbonized products. Different kilns offer varying sizes and capacities. Selecting a kiln that aligns with the required production volume is essential to meet business demands efficiently.
Technology:
Various carbonization kiln technologies exist, such as retort, rotary, and vertical kilns. Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages regarding efficiency, flexibility, and cost. Research different options and choose a method that suits specific business needs and preferences.
Budget:
Carbonization kilns can vary significantly in price depending on the size, technology, and features. Establish a budget and explore options that fit within financial constraints while still meeting essential requirements.
Location:
Consider the carbonization kiln installation location. Various factors, such as available utilities, environmental regulations, and land space, may impact the choice of kiln. Ensure the selected option is feasible for installation and operation in the intended location.
Environmental impact:
Assess the environmental impact of the carbonization process. Opt for kilns that incorporate emissions control technologies to minimize pollution and comply with regulatory standards. Choosing environmentally friendly options aligns with sustainable business practices and social responsibility.
Q1: What material is used to make a carbonizing kiln?
A1: Various alloys, refractories, and composite materials depend on the carbonization's particular characteristics.
Q2: What is the trend of carbonization kiln Technology?
A2: The trend is towards energy saving, environmental protection, automation, high efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Q3: How long does the carbonization process take in a carbonization kiln?
A3: The duration of carbonization can vary depending on the type of kiln and the materials being carbonized. In some cases, it may take from several hours to a few days.