(822 products available)













































































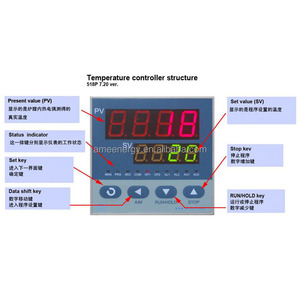




























































































































































The 1600 degrees resistance furnace is also referred to as the resistance furnace or the resistance heating furnace, which works by resistive heating. When electrical energy runs through the component, heat is generated due to the resistance. The heat produced is used to heat the workpieces. Heating elements can be made from materials like ceramics and alloys, capable of withstanding high temperatures. There are a variety of resistance furnaces that exist.
Some additional furnace types include the vacuum furnace and the high-frequency furnace. The vacuum furnace applies heat in a very high temperature and heats materials in a vacuum to reduce contamination. The gas cleaning heating system used by the high-frequency furnace heats steel scrap by using electromagnetic fields that create resistance and heat.
The lifespan of resistance furnaces strongly depends on maintenance schedules developed for various furnace parts or those developed around industry standards. Typically, resistance furnace manufacturers recommend periodic inspections following a set schedule. These inspections areas where they expect to find critical issues are the heating elements, control systems, insulation, and cooling systems. There's a furnace maintenance checklist that guides service teams or in-house maintenance teams during the inspections. They include, but are not limited to:
General maintenance practices for resistance furnaces include cleaning. Because contaminants are harmful to product quality, blocking the flow of electricity to certain parts of the furnace, lubricating movable parts, and adjusting controls is sought for a smooth-running resistance furnace. Manufacturers suggest the following tips:
Metallurgy:
1600 degree resistance furnaces are widely used in metallurgy for metal smelting, casting and other processes. Their high-temperature capabilities make them suitable for processing various metallic materials, including steel, iron, copper and alloys. Safety is critical in metallurgy. These furnaces are usually equipped with oxygen-deficient combustion technology and explosion-proof devices to minimize risks.
Ceramics:
In the ceramics industry, 1600 degree resistance furnaces play a crucial role in firing ceramic products like tiles, porcelain, crockery and more. Compliance with environmental regulations is essential. Resistance furnaces typically have efficient dust filtration and wastewater treatment systems to protect the environment.
Glass:
Glass manufacturing requires high-temperature resistance furnaces to fire glass products such as containers, flat glass and specialty glass. During the operation of resistance furnaces, attention should be paid to energy consumption and emissions. Regular optimization and maintenance can reduce energy waste and lower pollutant emissions, achieving a more eco-friendly production process.
Heat treatment:
Resistance furnaces undertake heat treatment tasks for metal parts like quenching, annealing and tempering. This process enhances the mechanical properties of metal materials. Technical guidance and operator training are crucial aspects to ensure the safety and quality of resistance furnaces. Proper usage and routine maintenance of the furnaces can effectively reduce the risk of accidents and improve production quality.
Laboratories:
Resistance furnaces are indispensable tools in the laboratory for material synthesis, melting, calcination and other experimental operations. They help researchers explore new materials and technologies. Throughout the entire production and operation phases, resistance furnace manufacturers emphasize quality control and technological innovation. They improve the design and production processes of the furnaces to meet customers' diverse needs and provide more efficient and reliable equipment.
When choosing a resistance furnace, some important factors to consider are the application, temperature range, energy source, control system, safety features, and regulations or standards.
Application:
The intended application is an important consideration when selecting a resistance furnace. Different applications may have specific requirements regarding heating elements, temperature range, size, and reliability. In manufacturing, metal annealing, glass melting, ceramics firing, and other specific industry applications may dictate the type and features of a resistance furnace suitable for the application.
Temperature range:
Temperature range is another crucial factor when choosing a resistance furnace. Some processes require high-temperature levels, while others need only moderate heat.A semiconductors manufacturing example may need a batch furnace with 1650degC for silicon wafers. On the other hand, metal heat treatment requires over 1600 degrees resistance furnace money for the processing to achieve the desired material properties.
Energy source:
The energy source of a resistance furnace can significantly impact its performance, operating costs, and environmental considerations. Some applications may be suitable for electric resistance heating, while others may require a gas-powered furnace.A gas resistance furnace works by passing an electric current through a metal wire or coil, which generates heat through electrical resistance. This heat is then used to heat the workpiece or material being processed. Electricity, on the other hand, is the energy source for induction and plasma furnaces. Induction furnaces use electromagnetic fields to heat conductive materials directly, while plasma furnaces use high-temperature ionized gas to melt and purify materials.
Control system:
The control system of a resistance furnace plays a critical role in determining its operational capabilities, precision, and ease of use. Many modern resistance furnaces are equipped with advanced digital control systems that offer precise temperature regulation, programmable profiles, and data logging capabilities. One trend is to have controls that interface with manufacturing execution systems for batch reporting.
Safety features:
It is important to note that the choice of resistance furnace also affects the safety features required. For example, a high-temperature resistance furnace may need stronger insulation, more robust materials, and additional safety features to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation at elevated temperatures.
Regulations or standards:
Regulatory standards are crucial when selecting a resistance furnace, as they need to be compliant with the relevant regulations and standards to ensure safe operation and meet specific requirements. Depending on the application industry, the resistance furnace must meet various environmental, health, and safety regulations. For example, resistance furnaces used in Europe must comply with the CE Marking requirements, which are safety standards set by the European Union. Similarly, resistance furnaces used in North America must meet the IEEE standards, which are technical standards set by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
Q1: What materials can the 1600-degree resistance furnace heat?
A1: The 1600-degree resistance furnace is designed to accommodate various materials, including metals, ceramics, and some refractories. However, verifying the compatibility with the specified temperature range is essential before heating any material in the furnace.
Q2: Can users control the atmosphere inside the resistance furnace?
A2: Yes, some 1600-degree resistance furnaces offer modifications that enable users to change the atmosphere within the furnace. These modifications include introducing inert gases or controlling the air exposure to the materials being heated.
Q3: What factors should one consider when choosing a resistance furnace?
A3: Some of the factors one should consider when choosing a resistance furnace are the maximum temperature required for the application, the size and capacity of the furnace, the heating rate, the type of control and automation features desired, and the atmosphere requirements for the processing materials.