(29712 products available)
































































































































































































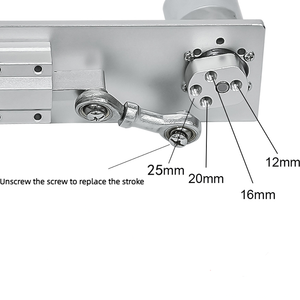






















Linear actuators are generally available in two types: mechanical and electromechanical. The latter type encompasses the miniature variants, including the 1 16 linear actuator, which typically features a smaller motor with a 1/16-inch shaft diameter.
Mechanical Linear Actuator
A mechanical linear actuator consists of a spindle and nut. The actuator's motor rotates the spindle, and the nut moves along the spindle linearly, converting the motor's rotational motion into linear movement. Mechanical linear actuators can be made from different materials, but metal components are necessary for durability. They also require an external motor to function. Some designs can accommodate different motor types (DC, stepper, etc.). A mechanical linear actuator needs a guide that's not fixed. It can be a screw or a rack and pinion.
Electromechanical Linear Actuator
This actuator relies on an electric motor for its movement. It either uses a lead screw mechanism, where the motor's rotation drives a screw that moves a sled or platform via a connected nut, or the more common rack and pinion, where rotational movement is converted to linear movement via a toothed rod.
As noted, miniature models are commonly specified with their dimensions in fractions of an inch (e.g., 1/16), but it is important to note that there are multiple size variants within the overall grouping that differ in strength, speed, and other parameters.
The 1 16 linear is used in various applications, primarily in the manufacturing and assembly industries.
Conveyor systems often use 1 16 linear components to move products and materials. In precise equipment such as medical devices or electronics, these components are favored due to their accuracy and reliability.
1 16 linear components are also used in product assembly businesses. Robotics and automated systems use linear motion to perform tasks precisely, such as picking, placing, welding, and assembling. These components offer reliable guidance and smooth motion for robotics joints and actuators.
Linear motion systems are typically found in soft film extrusion lines. They may be used in 3D printers, cutter tables, and slider curtains as a motion guide system to control the print head or build plate's position.
In machine tools, linear motion components are applicable in devices such as lathes, milling machines, and CNC routers. They are used for positioning cutting tools, workpieces, and precision machining operations.
When selecting a 1 16 linear for business needs, buyers should consider a range of factors. First, they need to explore the various types of 1 16 linear available, such as those made of steel, brass, plastic, and other materials. Second, they should assess the benefits of having 1 16 linear with 2D or 3D features and whether they require custom 1 16 linear for specific applications. Moreover, buyers should determine their intended application for the 1 16 linear, as this will help them to select the models with the right length and fit.
Additionally, buyers should select 1 16 linear based on the required levels of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. They should also choose 1 16 linear that is compatible with their existing systems and equipment in order to ensure proper functionality and performance. More importantly, buyers should opt for 1 16 linear with easy maintenance features if they have maintenance requirements. They should also consider 1 16 linear with the appropriate lubrication options and channels.
Buyers should select 1 16 linear 16 based on their noise levels and operational smoothness. They should also decide whether to choose 1 16 linear with standard or with linear ball bearing guides based depending on their budget constraints. Finally, buyers should source 1 16 linear from reputable suppliers and manufacturers. In the end, they should seek recommendations and reviews from other users to gather useful insights from other people with similar experiences.
Q: Why are it called 1 16 linear scale?
A: It is based on a fractional relationship between one inch and sixteen equal parts. One component is one inch long, and ideally, there should be sixteen components lining up to create an inch. Therefore, the name 1 16 is representative of how components fit in ideally one inch.
Q: Are all 1 16 linear scales the same?
A: No, linear scales can be made from different materials. Depending upon the material, it may be flexible or durable, digital or manual, and the accuracy may vary.
Q: What is the difference between a linear and a rotary scale?
Linear scale measures in a straight line, whereas a rotary scale measures angles or circles. Moreover, rotary scales are commonly used in applications requiring rotational feedback, while linear scales suit applications needing positional accuracy.